From 10 cents in 2010 to $66,000 in October 2021, Bitcoin has come a long way. It has seen such an exponential growth over the one-decade period that everyone has thought of investing in it at least once.
The situation is such that the rich are putting millions into it and the world governments are trying to regulate it. However, most of us aren’t clear about what bitcoin really is.
Is it a currency or an asset? How does it work? Who launched Bitcoin? How did it see such tremendous growth in only a decade? Is Bitcoin a scam?
This article answers many of your questions about Bitcoin. Read on to learn.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a cryptographically secured decentralised digital currency that can be sent directly from user to user on its peer-to-peer (P2P) network. It is created, distributed, traded, and stored on the blockchain.
Launched in 2009 by a mysterious person or group named Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin is not a physical coin. It is a digital currency whose existence is a public ledger of transactions. In other words, Bitcoin is a technology-powered token that functions as money.
Since this concept is completely new, it is mandatory to understand a few terms associated with Bitcoin.
- Decentralisation: Decentralisation refers to the process by which the power over the functioning of an entity is taken away from its authoritative group and delegated among a good majority of its stakeholders.
When we say that Bitcoin is a decentralised currency, we mean that it is not controlled by the government or the network of central banks worldwide; it is a technology that runs on codes and algorithms that nobody can influence.
Everyone can look into Bitcoin’s ledger of transactions to see how many coins are in circulation and which ID owns how much. Its records are public, unlike that of a bank. Moreover, every new entry is verified by a process called mining that allows hundreds of individuals to check its validity. - Bitcoin Public ledger: Bitcoin public ledger is a record of everything going on in its blockchain; that is, it records all the details of Bitcoin mining and transactions. The ledger keeps a pseudonymous account of its participants, the transactions executed among them, and their respective Bitcoin holdings.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P): Bitcoin transactions do not have to go through a central authority like a network of banks (unlike the mainstream cashless transactions). They can directly be transferred from one person to another. Such a transaction is called a peer-to-peer one.
- Digital coin: Bitcoin is not actually a physical coin but a virtual currency that exists as a set of computer codes. In other words, it is a piece of software that functions as money. So, when someone owns a Bitcoin, they don’t own a coin but the access to a specific address in Bitcoin’s ledger and the right to receive and send money through it.
- Pseudonymity: Bitcoin ledger stores each participant’s identity as a long computer-generated code of letters and numbers. So, although anyone can look at the ledger, no one knows how many bitcoins belong to whom. Thus, the currency is said to be ‘pseudonymous’.
Bitcoin uses cryptography to remain pseudonymous. That is, you might see how much money is transacted between what addresses, but you won’t know exactly who owns them. - Cryptographically-secured: Bitcoin blockchain uses cryptography to remain pseudonymous and hack-resistant.
The long computer-generated code in the ledger (also known as the public key) is generated using cryptography. Cryptography also facilitates decentralisation; so, if someone wants to hack the blockchain, they need to hack a huge network of computers on a cryptographically secured number. This requires so much time, energy, and effort that this is almost impossible.
Therefore, Bitcoin is a network with its own currency. When you buy bitcoin, you secure a place in the network. Now, you can make transactions worth even 0.01 bitcoin with anyone in the network. You can also provide them with a service and earn more bitcoins.
However, the catch is that you can also exchange these bitcoins for real-world money any day!
There are over 18 million bitcoins in circulation right now (out of a total of 21 million). They are being traded and transacted on a regular basis. Each time a new transaction wants to get into the ledger, Bitcoin miners verify it. The transaction, if approved, is recorded in the public ledger permanently; it can never be altered or removed. Also, the process of mining is further releasing more bitcoins into the network.
This security, along with decentralisation and other unique features, is adding to the worth of Bitcoin. Thus, it is growing exponentially and is by far the largest cryptocurrency in the world.
The Idea Behind Bitcoin
Back in 2008, money was fully centralised. Central banks and governments produced currency notes and coins and regulated their flow. This currency didn’t have any intrinsic value; it functioned only because the government backed it with a promise to pay the bearer the amount printed on a given piece of note or coin.

Thus, people trusted the government, and, in return, the government oversaw everything and ensured people’s faith. This system was efficient, but it had its own flaws.
- Control: In the fiat money framework, a small segment of people controls the flow of monetary value worldwide. As such, they had immense power over the others. Banks and governments could control the value of money and even declare it invalid overnight.
- Corruption: When a small segment of the population possesses most of the power, corruption comes into play; it is easier to bribe a few really powerful people than everyone.This is why we heard stories of bank employees and high officials forging millions for years without anyone reporting it.
- Mismanagement: Incompetent central authorities were another bane of the fiat money system. Inefficient governments and banks mismanaged the flow of value worldwide, causing several problems to the general public. For instance, incompetent banks might freeze your accounts or lead to transactional delays; also, their servers might just keep on crashing.
As such, there was a pressing need for a system of currency that is safe, trustable, and not centralised. What better way to do this than to go digital?
Since almost everyone is connected to the internet these days and the number is only rising, digital currency sounded the best way to give power to people.
However, then arose the problem of double-spending.
Double spending means using the same unit of money for two different transactions. For instance, you might buy a pair of trousers for $10, steal them when the shopkeeper is not looking, and then use the same $10 bill to purchase a shirt.
It is difficult to do this with physical money since getting caught while ‘stealing’ is high. However, a digital file can be easily counterfeited or hacked. This is why the idea of the digital coin has seen slow developments in the past many decades.
In such a situation, Bitcoin started as the world’s first decentralised virtual currency that solved all these problems through the method of cryptography and caused a massive revolution.
- Bitcoin is decentralised. Anyone on the network can mine bitcoins (whereas only the government can print notes) or look into its ledger. So, the power is in the hands of the whole of its network, instead of a select few. Here, you aren’t trusting a group of people who might turn out to be inefficient or corrupt but a secure algorithm.
- Bitcoin cannot be counterfeited or hacked because it is built on the new Blockchain technology.
- Bitcoin helps avoid the problem of double-spending because it is difficult to tamper with its ledger. One needs a huge amount of time, effort, and energy to do this.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
Now that you understand the idea behind Bitcoin, you must know how this virtual currency decentralises the monetary system and remains safe at the same time.
This is because it is built on a completely new technology, called the blockchain, that utilises cryptography to remain safe from hackers and malware.
Blockchain
Blockchain, as the name suggests, is a framework of blocks interconnected to form long chains. These blocks store information like contracts, transactions, bank loan statements, emails, partnership agreements, etc. Thus, a Blockchain is a publicly distributed ledger that stores details of deals between its participants.
The Bitcoin blockchain stores information about currency transactions. It keeps a pseudonymous record of its participants’ identities, transactions among them, and their Bitcoin holdings. This database can’t be copied, altered, or deleted; it can only be distributed.
Also, instead of being managed by a central administrator, the ledger is controlled by its users. Anyone on the internet can have a look at the ledger at any point in time. Every new information block is verified by other participants in the network by the process of mining.
A miner invests time, money and efforts into validating a block and receives payment of their services. The verified transaction is then recorded in the Blockchain database, and every participant computer (called a node) receives a copy.
This information is recorded permanently. It cannot be changed or deleted because blockchains are designed to retain the logs of all the transactions forever.
Another main feature of blockchain is that all the blocks are linked chronologically such that a change in one block alters all the connected blocks. This is because every block has a reference number called a hash.
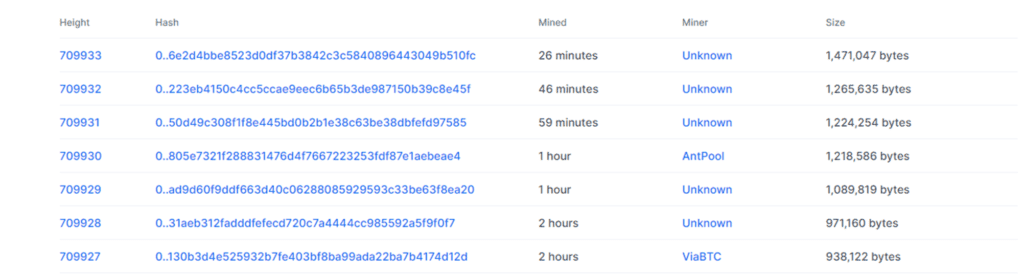
Hash is a computer-generated code of letters and numbers that represents a block in the blockchain. If the information contained in a block is changed even slightly, the network generates a new hash and, hence, a new block. Also, each block carries two hashes: its own and that of the preceding block. So, when one block’s hash is altered, it changes the hashes of all the proceeding blocks, thus, generating a new chain.
Since several thousand people have a copy of the original chain, the new one will be out of place. Thus, it will be discarded soon, restoring the blockchain back to normal.
Therefore, any information stored on the blockchain cannot be altered. Thus, it’s secure and hack-proof despite being in the hands of millions of people.
Mining
Bitcoin mining involves verifying and validating the addition of a new block into its Blockchain network. This process involves the release of more bitcoins into circulation and, hence, is called mining.
The people who indulge in mining are known as miners. They invest time, computer power, and lots of effort into verifying a new transaction and get paid in return.
Their remuneration takes place in two forms:
- Transaction fees: Each time a transaction is recorded in the Bitcoin system, a small portion of it goes to the miner.
- New bitcoins: Each time a new block transaction is verified, a new block is added to the chain. This releases a few bitcoins from the reserves into circulation. These bitcoins go to the miners as their remuneration.
After every 210,000 blocks are mined, the reward in each release is cut in half. This is called ‘halving’. In 2010, 25 bitcoins were released with each mined block. This number reduced to 6.25 in 2020 after the third halving. By 2140, all the 21 million bitcoins will be mined and into circulation. Then, the miners would have to rely on transactional fees only.
With the value of bitcoins soaring high, mining seems to be a lucrative profession. However, it is limited only to experts because of two reasons.
- It requires a lot of computer power and time: Bitcoin’s algorithm is designed to make the mining process artificially time-consuming. It runs a complex cryptographic program that demands time and proportionally high computing power. So, people are discouraged from spamming the network with spoofs and false transactions.
This also discourages hacking. Even if the information is changed 20,000 blocks back, it will generate a chain reaction that will take so much time to execute that someone would point out the mishap by then. So, unless one owns at least 51% of a blockchain, they can’t hack it. - It requires proof of work: Miners have to solve complex mathematical problems before securing permission to mind. The Bitcoin network regulates the difficulty level in such a way that the network grows by only a 1MB transaction every ten minutes. In this way, the whole system has enough time to come to a consensus regarding the transaction.
Bitcoin Transactions
Only a small percentage of Bitcoin network mines; the rest buy and sell it through cryptocurrency exchanges or purchase it to buy cryptoassets.
- Wallet: Wallets are software programs that use cryptography to access the Bitcoin blockchain. In other words, Bitcoin wallets let you buy bitcoins, access your holdings, and send them to other participants in the network. One can compare them to physical wallets that let you hold the regular fiat currency until you need it to make transactions.
- Keys: A computer-generated code is mentioned on the blockchain database instead of a participant’s personal information to retain anonymity. This code functions as the participant’s username and is called the public key. It denotes a wallet’s address.
Anyone over the internet can view this address. However, a wallet also has an associated private key that is only known to its user. This key functions like a password and lets the user access their wallet. Both these keys are generated by the computer using cryptography.
There are different types of wallets depending on how they keep their private keys secure.
- Hot wallet: Hot wallets are easy-to-use wallets that are connected to the internet. They store most of your details (including the passwords and PINs) online and therefore are not well-secured. However, since they eliminate the need to switch from offline to online or connect any third device, they are best for the ones who use bitcoins to buy things. Three types are hot wallets are:
- Mobile wallets: They can be installed on Android or iOS devices and are best for retail transactions.
- Desktop wallets: As the name suggests, these are installed on desktop devices.
- Web wallets: Web wallet services are completely online in nature. They can be accessed from any device at any time (just like one’s email).
- Cold wallet: Cold wallets are not connected to the internet. Here, all the user’s details are stored offline, either on a device or on a piece of paper. While cold wallets are much more secure than hot wallets, they aren’t convenient for transactions. Thus, they are mostly used to store large amounts of Bitcoin holdings. There are two types of cold wallets:
- Paper wallet: This is the oldest kind of wallet. Here, a person writes their details (keys) on a piece of paper and keep it secured.
- Hardware wallet: A hardware wallet is a USB-resembling device that stores the wallet details of a user. The device has to be plugged in to access the wallet.
Why Does Bitcoin Have Value?
Bitcoin was launched as the world’s first virtual currency. At the time of its launch, it had no value. One bitcoin sold for around 10 cents for the most part of 2010, that is, more than a year after its launch.
Then, as people started to realise its significance as the world’s first digital currency, its demand grew.
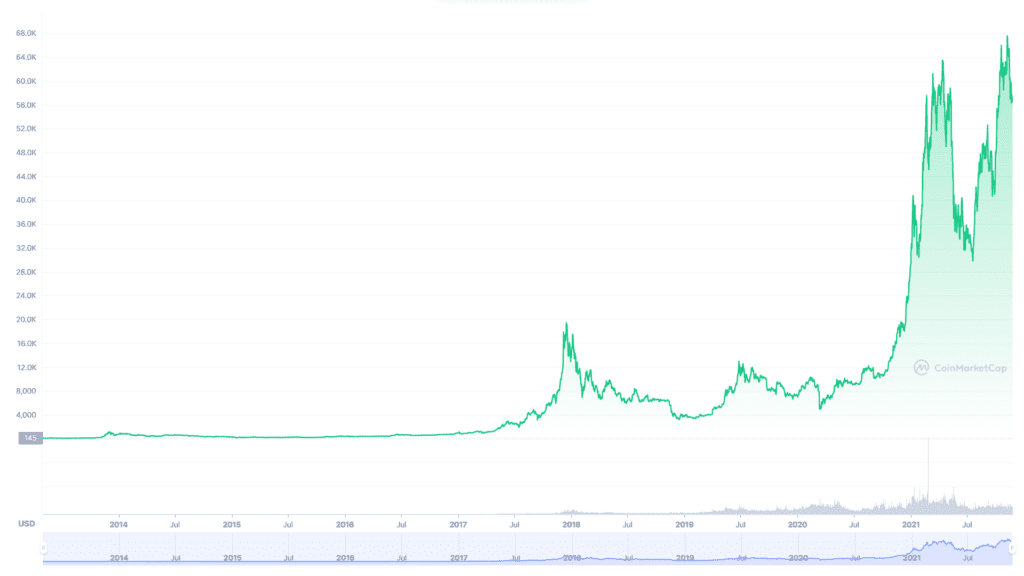
Several of its transactional use cases came into play, further increasing the currency’s value. It started to seem that Bitcoin may retain this value in the long run and act as a trustworthy store of value. Also, it’s safe and divisible. When we divide a bitcoin down to eight decimal places, we get a unit of the cryptocurrency called Satoshi.
Thus, the demand for Bitcoin grew further up. Given its constant supply, its price started to rise so much that one bitcoin is worth more than $60,000 at the time of writing.
However, the market holds speculative interest for most of the participants. Since the value of Bitcoin fluctuates every day in one of the most volatile markets, one can’t be sure of its sustainability.
But this hasn’t caused people to lose interest in the coin. If anything, more are joining each day, thus, tipping the balance of demand and supply and increasing Bitcoin’s value.
How Can You Make Money from Bitcoin?
Bitcoin cannot be used for most retail transactions just yet, though many merchants do accept it as an alternative to fiat. However, since they have a monetary value, possessing them is equivalent to owning an asset, an income-generating asset whose value might appreciate with time.
Here are the major ways by which you can make money from Bitcoin.
Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining releases new coins into circulation. These coins are awarded to the miners as a remuneration for their services. However, most of the bitcoin owners don’t indulge in mining because of the immense technical, intellectual, and monetary investment associated with it.
Bitcoin Trading
Cryptocurrency is volatile. The value of Bitcoin fluctuates every day just like stocks and FOREX. So, bitcoin owners meet as buyers and/or sellers on a platform (known as an exchange) to trade bitcoins and earn profits.
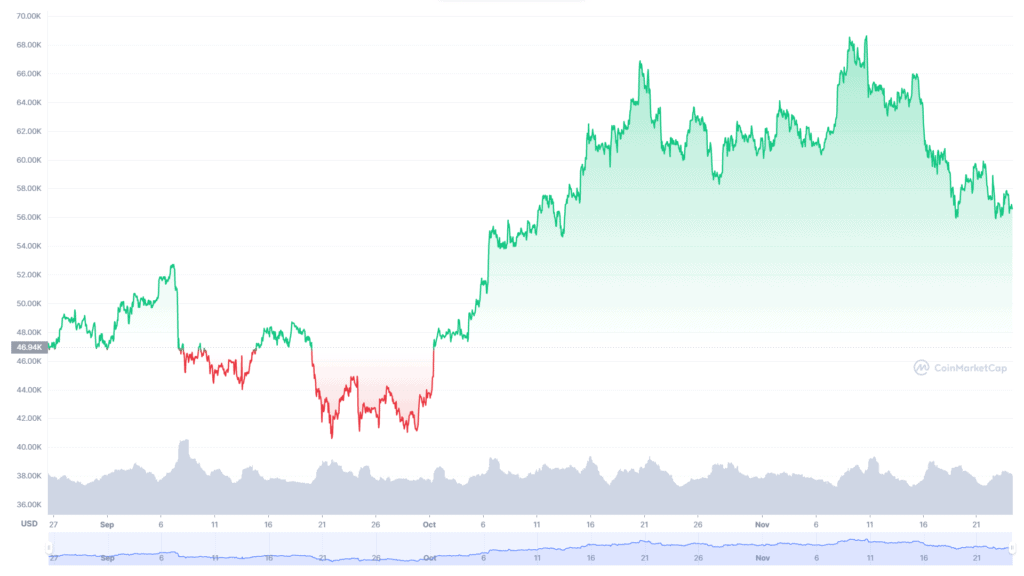
There are two major problems associated with Bitcoin trading:
- Unlike stocks, the market is unregulated. So, several exchanges violate their withdrawal policies and manipulate the general masses.
- Bitcoin market is highly volatile. While this might imply to exponential profits, one wrong move can have you lose thousands of dollars.
Bitcoin Investing
Investing in Bitcoin involves buying and holding it for a few weeks, months, or years before selling it for a profit.
Bitcoin investors allocate a portion of their portfolio to Bitcoin; they generally buy it when it’s going low and wait for it to grow in value. They call themselves “HODL’ers”.
What Are The Advantages Of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was launched to replace the current monetary system. It has several advantages as an alternative form of currency.
- Bitcoin is a decentralised currency. There is no central authority that controls its value or circulation.
- Anyone can look into Bitcoin’s ledger but only the miners can add new blocks. These miners are accountable and have to provide ‘proof of work’ before securing this right.
- Even though anyone can look into Bitcoin’s ledger, transactions are recorded in a pseudonymous fashion. That is, only the public keys are provided with no other detail of the participants.
- Bitcoin is deflationary. The number of bitcoins released into circulation decreases every four years, thus keeping its value up.
- More and more people are trading and investing in Bitcoin. Since the market is volatile, there is a huge potential for high returns.
- Bitcoin facilitates easier and cheaper international transactions.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Bitcoin?
While the currency has several advantages, it also has its disadvantages.
- The bitcoin market is volatile (even more than FOREX and stock markets). While one may earn 10x returns immediately, one might also lose millions.
- Since Bitcoin is unregulated, its exchanges are also not controlled by the authorities. Therefore, there is a huge chance of frauds and scams on such platforms.
- Although Bitcoin was launched as an alternative to fiat money, it cannot be used for general and retail transactions because of huge transaction time and processing charges.
- Since the authorities do not monitor Bitcoin, it is used for illegal transactions in the black market and over the dark web.
- Bitcoin is based on the new Blockchain technology. One may find irreparable bugs in it.
- As new cryptocurrencies are being launched every month, people might shift from Bitcoin soon.
- There have been instances of people losing their wallet passwords and getting locked out of it losing millions.
What Is The Current Status Of Bitcoin?
Currently, there are around 18 million bitcoins in circulation. After the third halving in 2020, miners get 6.25 BTC per valid block mined. The last bitcoin will be mined in 2140. After this, the miners would have to rely only on transaction fees as remuneration.
Although the currency didn’t get enough credit at the time of its launch, it has grown since then. The first bitcoin transaction happened on May 22, 2010, when a Florida resident exchanged 10,000 bitcoins (worth over 600 million at the time of writing) for two Papa John’s pizzas.
Since then, Bitcoin has found use in facilitating low-cost money transfers, especially anonymous ones. Various other cryptocurrencies (like Ethereum, Dogecoin, Cardano, etc., collectively known as altcoins) have also come up; all of them were inspired by Bitcoin.
Also, Blockchain technology is being widely used and developed. Several startups have started dealing in the Blockchain and Crypto space. The field is seeing an unprecedented boom, with new innovations coming in every day. Now, one can use cryptocurrencies to purchase flight tickets, book hotels, buy artworks, or create a whole game world.
However, owing to anonymity and decentralisation, Bitcoin is also being used to fund illegal activities. So, governments around the world are trying to regulate it. Many countries have already started taxing cryptocurrencies like other investment vehicles.
Frequently Asked Questions
The advent of blockchain and Bitcoin has everyone intrigued. Here’s a list of the top frequently asked questions and their answers relating to Bitcoin
What Is The difference between Bitcoin and Altcoins?
All other cryptocurrencies than Bitcoin are known as altcoins. Ethereum, Dogecoin, Cardano: all are examples of altcoins. They were built on Blockchain technology after the success of Bitcoin and utilise other specifics to reduce the time needed for the addition of blocks.
How Do I Earn Money From Bitcoin?
Besides mining new bitcoins, one can purchase them, hold them for some time, and sell through an exchange when their price has risen.
When bitcoins are sold within a day, it’s called Bitcoin trading; when it’s held for a period of a few days, weeks, months, or years, it’s called investing in Bitcoin.
Why Is Bitcoin Exploding In Value?
As the world realised the importance of Bitcoin, people started considering it as ‘the next big thing’. Thus, its demand started to grow exponentially. Given that its supply is not increasing at the same rate, Bitcoin is exploding in value following the law of demand and supply.
What Are The Risks Associated With Bitcoin Investing?
The major risk associated with Bitcoin is high volatility. People have lost millions in cryptocurrency since the market is the most speculative (even more than FOREX and the stock market). Moreover, one cannot be sure of its future validity. The currency (or even the whole technology) might prove to be outdated in a few more years.
Also, most people dealing in Bitcoin do not have much idea about it. This increases the chances of fraud. In fact, several fraud Bitcoin mining farms have scammed their investors.
Even if the blockchain is hack-proof, wallets and exchanges aren’t. People have lost millions when unreliable exchanges have been hacked.
Who Is Satoshi Nakamoto?
Bitcoin’s whitepaper was released under the name of Satoshi Nakamoto, an anonymous person or group of persons credited with creating Bitcoin. No one knows who they really are, where they live, or how many bitcoins they own. While various individuals have claimed to be Satoshi Nakamoto, nothing has yet been validated.
How Many Bitcoins Are There?
As of now, there are over 18 million bitcoins in circulation. The amount will keep on increasing until the cap of 21 million is reached in 2140.
Should I Invest In Bitcoin?
While Bitcoin is one of the best-performing assets as of now, it is completely different from anything that the world has seen before. Not only is the market extremely volatile, one cannot be sure of its future. Therefore, it is recommended that you invest in Bitcoin (or any other crypto asset for that matter) only if you have a huge risk appetite. Also, be thorough with your research.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think of this article on what is bitcoin in the comment section.
A finance enthusiast, literature beau and lifelong learner. Working her way up the success ladder and her personal philosophy textbook, Kavvya believes that a good conversation is worth more than a good book. When not working, she can be found reading, writing and engaging in long walks.









