Google handles over 63,000 searches every second. This translates to at least 3.8 million searches every minute, 228 million searches every hour, and 5.6 billion searches every day.
In short, people search a lot.
But the problem is – 75% of these people never scroll past the first page of search results. That is, even if you have the best website, if it isn’t on the first page of Google, you’re non-existent for a lot of internet users.
Some companies and individuals (who have money) overcome this problem by paying for an ad on Google. But that’s not a permanent solution. 70% to 80% of the search users completely ignore such paid advertisements.
This is where search engine optimization comes to the rescue.
You might have heard about it in one of those digital marketing webinars or tutorial videos. But not many actually know what it really is and how it works. Well, fret not. Here’s a detailed guide on SEO for beginners where we dig deep into –
- SEO Definition (What is search engine optimization?)
- Search Marketing (SM) vs. Search Engine Marketing (SEM) vs. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- SEO Types
- How To Do SEO?
What Is SEO?
SEO or Search Engine Optimization is the practice of optimizing the content, webpage, and website to drive more traffic from search engines’ search results by ranking at a higher position organically.
Few keywords and key-phrases that you should note in the above definition of SEO –
- Optimizing the content, webpage, and website: SEO involves understanding how search engine works and using that knowledge to optimize the content posted, the page it is posted on, and the website over-all.
- Drive more traffic from search engines’ search results by ranking at a higher position: The main goal of SEO marketing strategy is to rank the website higher in the search results for targeted keywords, which brings in more targeted traffic to the webpage and/or website.
- Organically: SEO is an organic digital marketing strategy. It doesn’t involve you paying Google to rank you higher. It involves you optimizing your content according to what the search engine desires to get discovered through the search engine’s results.
In simple terms, SEO is an organic strategy to rank high in search engine results.

Importance Of SEO
93% of online experiences begin with a search engine. If this doesn’t make you understand the importance of SEO, here are some other facts –
- Search engines drive 300% more traffic to websites compared to social media.
- The close rate of SEO leads is 14.6% compared to only 1.7% of outbound leads (like print ads).
- 70-80% of search users ignore paid ads completely.
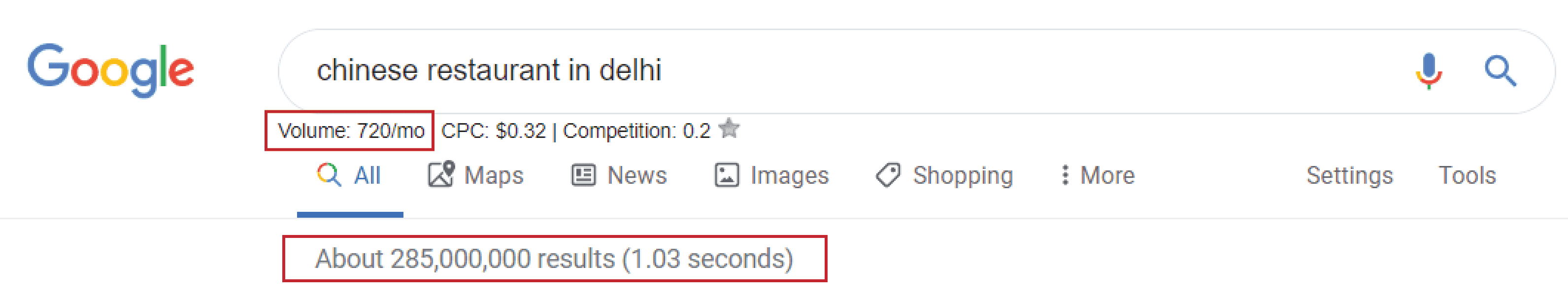
Let’s take an example of the query – ‘Chinese restaurant in Delhi’.
Every month 720 people search for this query. But even though this is a specific query, there are 285,000,000 results. Now, considering the facts that –
- The top three results enjoy 60% of the clicks, and
- 88% of pages are invisible in Google.
…only 10 out of those 285 million businesses who were able to optimize their website very well succeeded in getting attention in the search engine results.
Other than the fact that SEO helps you prove to Google that your page is most relevant for a keyword, here are more reasons why SEO is important –
SEO Is A Very Efficient Lead Collection Strategy
When compared to other outbound lead collection strategies like cold calling or direct mail, SEO costs 61% less. Moreover, 57% of B2B marketers believe SEO generates more leads when compared to other marketing strategies.
SEO Helps You Convert More Leads Online
SEO helps you target specific keywords that you can sync with your target audience’s buying cycle. Moreover, leads from search engines have a close rate of 14.6% compared to outbound leads which have just a 1.7% close rate.
Good SEO Is A Big Competitive Advantage
Considering the fact that 90.88% of the web pages on google search results are almost invisible, good SEO is a significant competitive advantage, especially if you get your customers online.
Even if your customer acquisition process ends on offline channels, good SEO aids your discovery online during the research phase of the buyer’s decision-making process.
Paid Search Isn’t As Good As It Seems
According to Brightedge, organic search drives 51% of traffic while paid search drives only 10% for both B2B and B2C businesses. That’s 5x more effective.
SEO vs. SEM vs. Search Marketing
More often than not, people tend to confuse these three terms – search marketing, search engine marketing, and search engine optimization. Even though they sound similar, there’s a considerable difference among these three terms –
Search marketing is the practice of using paid and unpaid tools and strategies to gain traffic and visibility on search engines. It’s an umbrella term that covers both SEO and SEM.
Search engine marketing is the practice of using paid ads to gain traffic and visibility on the search engine. It is often referred to as Pay Per Click (PPC) ads.
Search engine optimization is the practice of optimizing the website, webpage, and content to gain traffic and visibility on search engines organically without paying them.

How SEO Works
Now, the main task of an SEO marketer is to make the webpage so compelling that Google and other search engines rank them on top automatically. But before hopping on to the SEO tutorial, one needs to know how exactly do search engines work and what factors do they use to rank the webpages.
How Do Search Engines Work?

Search engines have three primary functions –
- Crawl: Crawling is a discovery process where search engines send robots to search for the content all over the internet. These robots crawl one page and use links on that page to hop on another and so on. Besides this, the crawlers also crawl pages submitted to the search engine by website owners.
- Index: These search engines store and organize content while crawling. The process goes like this – once the page is found, the search engine renders it just like a browser would have; it then analyses the page and its contents and stores it in its index.
- Rank: Once the webpages are indexed, they are ranked in the search results according to their relevance. Every search engine has its particular algorithm which decides the relevance of each indexed webpage according to the search key-phrase. And this algorithm changes very often. Google, for example, even uses artificial intelligence to decide the relevance of search results.
Moz explains all these three functions in detail in this article.
Search Ranking Factors
Now, a webpage ranks well if –
- It can be crawled easily and at a faster rate,
- It can be trusted,
- It provides good user experience, and
- It has all the relevant content, according to Google and the reader.
In theory, this seems pretty simple. But these four umbrella aspects cover over 200 different factors that Google uses to rank each search result. Now, we’ll talk mostly about Google as it almost has a monopoly in the search market, enjoying 87.96% of the market share.
Easier To Crawl
The first task of an SEO expert is to make it easy for Google to crawl and index the website. The following factors make crawling and indexing easy –
External And Internal Linking
Google’s spiders (robots) make use of external links on one site to hop on to another site and then use its internal links to crawl its internal pages.
Using a good linking strategy makes it easy for Google to crawl and index the pages.
Technical Ease
Google has a dedicated platform for webmasters to submit their websites. It’s called Google search console (webmaster tools). The site is submitted in the form of a sitemap (an organized structure of all the posts, pages, and other content on the website).
Moreover, websites also include a file called robots.txt which tells the search engine crawlers about which pages and files it is allowed (or not allowed) to request from a site.
Organized Structure
Site structure is how you organize your website’s content. It includes grouping related content under the same taxonomy, category, and tags, etc. This structure makes it easy both for the search engine and user to navigate through your website.
Trustable
In the simplest terms – a trustable website is one that is secure from hackers, malware, and virus; whose content is reliable; and whose owner isn’t blacklisted because of spamming or scamming.
Secure Website
Search engine trusts websites with HTTPS certificate more than those who don’t have this certificate. HTTPS means that the data shared with the website remains with the website, and no one else has access to it.
Other than this, it also makes sure that the website is not infected with malware, adware, and other viruses which will affect the user in any way.
Domain Age
Old domains are trusted more. According to Google, the website which has been in existence for more than a year has more authority than a newly made website.
Domain History
Google also considers what the website used to deal in previously. If a website used to sell toys a few years back and now instantly pivoted to writing on business and marketing, it makes it less likely to be trusted.
Whois
Whois information is the information about who owns the website. If the owner of the website was previously tagged as not trustable or spammer, his new website is also less likely to be trusted. Moreover, websites with private Whois information are also less trusted than websites with public whois information.
Contact Information
Adding a contact-us page increases the trust factor of a website in the eyes of the search engines.
Updated website
Update website means it uses the latest code structure and operates on the latest version of the platform, which makes it hard to be hacked. This increases its appeal in the eyes of Google.
Terms of Service & Privacy Policy
Adding terms of service and privacy policy pages is also appreciated by search engines like Google as they consider them to be a factor of trust.
Not Spam
A website that is created just to link to other websites and not to provide any value to the user is considered to be spam. Google uses its special algorithm to assign a spam score to each website and webpage.
Credible Content
Google uses AI to scan the content, keywords used, outwards links, and inward links to check the credibility of a webpage. A website is usually considered credible if –
- The content is original (not copied from other websites)
- It includes all the major keywords and other keywords related to it.
- It is free of grammar and spelling errors.
Good UX
Google’s aim is to provide a seamless experience to the users who use its search engine. This also includes providing them results that give them equivalent experience and quench their thirst of knowledge.
User-friendly layout
A website with a user-friendly layout, where the content can be read easily without any disturbance or pop-outs, is given more preference than the website with not so good layout.
Responsive
Most of the searches on Google come from mobile. Hence the search engine now rewards websites that are optimized for mobile and demote those who aren’t.
Fast
According to Google, 53% of mobile users leave a site that takes longer than three seconds to load. This makes speed to be an important factor considered by Google while indexing and ranking the websites.
Multimedia Content
Adding multimedia content like images and videos to the textual content makes it more engaging. Hence, this, too, works as a ranking factor.
URL structure
Since the URL structure is shown on the search result, Google prefers it to have the targeted keyword to help users know what the article will be about before clicking it.
Up-to-date content
Up-to-date content proves to be more relevant to users and hence is usually given preference in Google results.
Citation and links from credible sources
An article with links from a high authority website is preferred to a similar article without such links.
Time spent on page
Google also estimates the bounce rate and time spent on a webpage. If the bounce rate is low and the time spent on the page is high, it automatically considers that page to be relevant.
Search engines also consider the authority of the webpage over social media. The number of social shares affects the ranking of an article on Google.
Types Of SEO
Doing search engine optimization is not as easy as you think. The practice differs based on –
- The type of website
- Your motives
- Techniques used
- Location served
- Targeted type of search, and
- Device used
Based On The Type Of Website
Different websites require different types of efforts by SEO marketers. These are –
- Ecommerce SEO: The objective of eCommerce SEO is to get products on top of the search results whenever someone searches for them or their parent category. For example – Best book for entrepreneurs
- Blog SEO: Blogs include several keyword-focused articles. The objective of blog SEO is to rank those articles high in search engine results according to their focus-keywords.
- Business SEO: The objective of business SEO is to get the business name and website on top whenever someone searches for the brand name or the products it deals in. For example – Chinese restaurant in Delhi.
- Personal SEO: Personal SEO is done to highlight a personal profile, business profile, or portfolio website whenever someone searches for his name or the industry he operates in. For example – fashion photographer in Delhi.
Based On Motives
Different Webmasters and SEO marketers have different objectives for their websites. These objectives could be to rank the website for the long run or just get a high rank for a day, week, or few weeks. To fulfill the same objectives, they use different SEO practices which are classified as –
- Black Hat SEO: It’s the unethical practice of using SEO tactics that are against search engine guidelines, to rank the website higher in the search results. These websites, even though get ranked high in the search results, are usually penalized by the search engines after a few days. Black hat SEO techniques include – keyword stuffing, cloaking, poor quality content, poor quality links,
- White Hat SEO: White Hat search engine optimization is the practice of using ethical SEO techniques that are in line with the search engine guidelines, to rank the website higher in the search results for the long run. It involves practices like getting webpages to load fast, developing high-quality content, making the website easy to navigate, and getting organic links from other websites, etc.
Based On Optimization
SEO isn’t limited to the own website or just on the content page. It involves optimizing the website both on-the-website and off-the-website to get the best results.
- On-Page SEO: Also called content SEO, on-page SEO the practice of optimizing content with relevant title tags, meta descriptions, headlines, in-depth content, focus keywords, long-tail keywords, and formatting to rank higher and get more traffic from search engines.
- Technical SEO: Technical SEO is the practice of optimizing the website and individual webpages to make them easier to crawl and index. It involves optimizing robots.txt, making the website fast, securing the website with SSL, developing the responsive version of the website, registering and submitting to search consoles of search engines, etc.
- Off-Page SEO: Off-Page SEO includes the actions taken outside the website that impact its rankings in search results. These actions and practices include – developing business page on Google, getting PR links, getting organic links from other websites, having a good social media presence, website content being shared on social media, website content being used as a source on other websites, etc.
Based On Location Served
There is an increase in location-centric searches and search engines have tweaked their algorithms to serve the same.
- Local SEO: It involves SEO strategies used to increase the visibility on targeted location-based search queries. This technique is often used by local brick-and-mortar stores to get more visibility online whenever a potential customer searches for its brand name or the industry it operates in. For example, SEO practices to rank for ‘Chinese Restaurants in Delhi’.
- National SEO: Google.in’s search results differ from Google.com’s search results. National SEO is the practice of ranking high on a national level.
- Global SEO: Global SEO is the practice of optimizing the content for a multitude of regions worldwide. Businesses which have a target audience in different countries often use this SEO technique to rank high on country-based searches. For this, they either develop country based sub-domains or translate their content according to the country the user resides in.
Based On Type Of Search
With the advent of digital assistants like Google Assistant, Alexa, Siri, the number of voice searches has increased substantially. Besides this, people also search for images and videos which require SEO of their own.
- Textual Search Optimization: Optimizing to rank high on textual search queries refers to textual search optimization.
- Voice Search Optimization: Optimizing to rank high on a voice search query is voice search optimization.
- Image SEO: Optimizing website images to rank high on search queries for images is image SEO.
- Video SEO: Optimizing the videos to rank high on video search engines and video search queries on normal search engines is Video SEO.
Based On Device Used
Google has different crawlers for mobile and desktop searches. It has even released guidelines for voice searches. This information is often used by SEO experts to rank their webpages for device-based searches.
- Mobile SEO: Developing a mobile-responsive website and following the guidelines of search engines to rank on mobile search engine queries is mobile SEO.
- Desktop SEO: Optimizing the website to make it easy for desktop crawlers to crawl and index the website.
- SEO for Digital Assistants: Following the SEO guidelines for digital assistants and including required structured data to ensure search engines that the website is optimized for digital assistants is SEO for digital assistants.
How To Do SEO – SEO Tutorial
Now that you know all the different types of SEO that exist in digital marketing, it’s time to move on to explaining how to do SEO effectively and efficiently.
Find The Objective
The first step requires you to decide on the motive. These questions might help –
- What’s the type of website you wish to optimize?
- What content does it produce?
- Is it for the long term or just for a gig?
- Is there a specific geographic region you want to optimize for?
- What device do you want to optimize your website for?
Once these questions are answered, move on to the next steps.
Start With Technical SEO
Start with making it seamless for search engines to crawl and index your website. Follow these steps for technical SEO–
- Develop a website sitemap.
- Submit your website’s sitemap on the search engine’s webmaster tools.
- Create a Robots.txt file with a sitemap link in it.
- Make your website easier to navigate.
- Make it fast to load
- Specify a URL structure with target keywords in it.
- Make the website mobile responsive.
- Implement structured data markup (Schema markup)
Work On Compelling Content & On-Page SEO Optimization
Find the keywords you want to rank for. Once done, develop compelling content that includes these keywords and other related long-tail keywords. Long-tail keywords are usually the keywords Google suggests you while you’re searching for that keyword. Besides this, these keywords also appear in the people also ask dialogue box and at the end of every result page.
Compelling in-depth content is the backbone of search engine optimization. This task involves you to check on what already ranks on the selected keywords and how you can make your content better. Write content that provides utility to the audience but, at the same time, tells search engines about the focus keyword you want to rank on.
But remember not to overoptimize. A rule of thumb is to keep the volume of focus keyword to be between 1 to 2 percent. That is, if your article length is 1000 words, it’s a good practice to include your focus keyword at least 10 and at most 20 times. A single or twice occurrence of long-tail keywords is also considered to be a good practice.
Also, try including the same focus keyword in the heading, URL, and meta-description to optimize your content even more.
Focus Off-Site And Build Authority
Off-page search engine optimization refers to those efforts you make to convince Google that other people also think that your content is worth ranking. This involves getting backlinks from other high authority websites and increasing the social shares of the article.
Here’s a good guide by Brian Dean on how to get high-quality backlinks. I’d suggest following it to make your off-page SEO game stronger.
Establish A Control Process
Now, this is a crucial step that most people usually forget. Search engine optimization isn’t a one-week process. It requires time to rank content high in the search results.
This step requires you to set up a control process where you check what’s working and what’s not. Start with the end in mind – the goals, and measure your progress towards achieving them using your current strategies. Repeat this strategy often and modify your strategies if necessary.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on search engine optimization in the comments section.
A startup consultant, digital marketer, traveller, and philomath. Aashish has worked with over 20 startups and successfully helped them ideate, raise money, and succeed. When not working, he can be found hiking, camping, and stargazing.









