Admit it. You have pondered over this question while casually searching for some cat videos. Then you eventually gave yourself the “Hey, these guys show tons of ads. They probably earn enough money from it.” Then when with time when the internet went haywire over privacy concerns you gave yourself the “Hey, if I am not paying, I probably am the product.”. To be fair, your hunch wasn’t way off target. But to put things to perspective, we are going to tell you EXACTLY what is the business model of Google and how does Google earn money.
How Does Google Make Money?
Google handles 1.2 trillion search queries per year and has partnered with over 2 million websites which have a reach to over 90% of people on the internet. Imagine advertising to such a huge market. In Q3 of 2018. Google’s revenue amounted to a whopping 33.6 billion USD.
And guess what?
In 2018, advertising revenue from Google sites amounted to 70.9% of the company’s revenues and advertising revenue from Google network sites amounted to 16%.
So the base answer would be advertisements. A lot of them.

How Does Google Make Money From Advertisements?
There are three components of Google business model that aid Google to help advertise: AdWords, AdSense and AdMob.
- AdWords is the advertiser targeted platform which lets them develop and launch ad campaigns on Google Search and Google Display Network. It decides what advertisements are to be displayed on the Google webpage and on partner websites.
- AdSense is the publisher oriented platform which lets the publishers make money by putting advertisements on their websites. These publisher websites form a part of the Google Display Network.
- AdMob is the same as AdSense except it is for mobile applications.
What is Google Ad Bidding And How Does It Work?
Google ads campaigns can be categorized into two types –
- Search Network Campaign – Google Search Campaign allows you to display your advertisements in the Google search listings. These ads are triggered when someone searches for the targeted keyword.
- Display Network Campaign – Google Display Network Campaign allows you to display your advertisements on Google apps like Gmail, Youtube, as well as millions of other websites and applications which use Adsense and AdMob to monetize themselves. These ads can be targeted according to the users’ activities on your website and the targeted keywords (will be shown on the most relevant content).
Usually, more than one advertiser bid for a certain keyword (search network and display network) or a placement (display network) and the winner is decided by Google triggering an auction. The winner of this auction is decided by looking into two key metrics — the CPC bid (the maximum amount you’re willing to bid for a click on the ad) and the quality score (a metric which decides how relevant your ad is to the user). The product of these two metrics results in the ad rank of the advertisers and the one with the best ad rank wins the auction.
Here’s an example to explain things further –
Advertiser | Max Bid (CPC) | Quality Score | Ad Rank |
A | $2 | 10 | 20 |
B | $3 | 6 | 18 |
C | $5 | 3 | 15 |
In the above example, even though advertiser C put the maximum bid, advertiser A won the auction as his ad was considered to be a right fit for the keyword/placement.
Now,
How much will actually advertiser A pay per click for this ad?
Earlier, this bid was generally taken in the form of a generalised second price auction system which was an extension of the Vickrey auction where the winning bidder paid the second-highest bid, all in undisclosed bidding, so no one knew what their competitors had bid for. The formula for this method was –
Price Paid = Second highest ad rank/Your quality score + $0.01
This means advertiser A would have paid: 18/10 + $0.01 =$1.81 per ad click.
However, Google has recently moved to first-price auctions where the advertiser now pay what he bade for.
This means advertiser A will now pay: 20/10 = $2 per ad click.
The quality score plays a very important role in ranking the advertisements.
Imagine a bid for washing machines, multiple advertisers bid for it. The advertiser bidding the highest bid (say: Amazon) gets the top spot because it also had a good quality score.

However, when you change the keyword to the top loading washing machine:

Even though if Amazon bade more, the top-loading washing machine keyword would have been more relevant with the Whirlpool ad so Google puts the relevant more specific ad based on the quality score.
The incorporation of the quality score does make sense as Google targets the potential market only. This makes it the best platform for advertisers to improve their reach. Of course, Google has a lot of background data about the users it is going to show the advertisements to. It has access to your cookie data and search history for starters.
Google Adwords
While advertising through Google AdWords, an advertiser has to pay only if their advertisement has been clicked on a publishing partner’s website. So the charge boils down to cost per click.
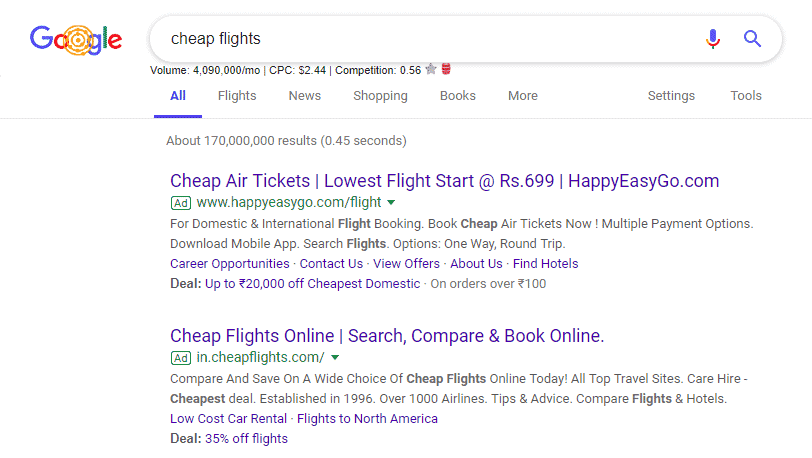
This is a foolproof method for advertisers to know if their reach is getting affected by Google AdWords.
Based on this information, let us guesstimate the profit:
There are around 4,090,000 searches per month for ‘cheap flights’ in the USA and the estimated CPC is $2.44. So even if we take 40% clicks on the ads, it brings us to around $3,991,840 which is a lot of money in my opinion. Again this is just one advertisement for a particular keyword. Imagine the cluster of keywords and the costing brought up together. This brings some huge figures.
Google Shopping Ads
When Google thinks that a particular search query is done with the intent to buy, it brings up Google Shopping Ads.
You must have encountered Google Shopping ads. They look something like this:

Google shopping ads are great at picking target shoppers as the ad format is more direct and the pricing is more conveniently displayed.
Google Display Network

The fun thing about Google Display Network is, it puts out partners to publish its advertisements.
Advertisers constantly bid for the Ad space a partner provides on their website or application. Of course, since it is the partner’s property, they can choose which ads to keep, which categories, format and text style to the advertisement is best suited to go with the website’s layout. The partners can even add Google-like search (with ads) on their website to earn a bit more.
In return, Google pays the partner website every time the advertisement is viewed or clicked on by a user. The revenue share between the partner and Google is in the ratio 3:2 (for search ads, it is 51:49). Youtubers, however, are paid in the ratio 11:9.

The amount of money a partner website (Adsense) and applications (AdMob) earns from a click depends upon factors like keywords, industry and the advertisement which is clicked on. If the hits on your website are too high, you can be a premium AdSense partner with a higher revenue share.
Revenue From Other Sources
Google has expanded its business model to a lot more than just search. Likewise, the revenue model has also expanded and now includes revenue from Google Maps, G Suite, Google Cloud, Android, Play Store and its acquisitions like Dialogflow, Kaggle, etc.
Revenue from Google Maps
Google maps run on a path similar to the parent company and earns some of its revenue from advertisements (local search ads and promoted pins). However, Google maps gets most of its revenue from its API which is used by big corporations like Uber, Trivago, Airbnb, Pokemon Go etc. The pricing of the product is pay as you go and the developers also get a recurring $200 credit on their billing account each month to offset their usage costs.

The brand has also partnered with cab-hailing companies like Lyft where the available cabs and their prices can be discovered on the Google Maps application.
Revenue From Google Translate
Just like Google Maps, Google Translate is a free-to-use application for individuals and makes money when businesses use its API.
The cloud translation API supports more than one hundred different languages, comes with automatic language detection, and comes in the form of easy-to-use Google REST API where the developers just have to send HTML documents and get back translated text.
The product is priced monthly based on usage.

Revenue from G Suite
G Suite is a brand of cloud productivity and collaboration tools including Gmail, Calendar, Drive, Hangouts, Docs, Sheets, Slides, Sites, Jamboard, App Maker and Vault. The brand operates on a freemium business model where the individual user gets a limited cloud space and features for free but has to pay when he wants more or wants to use it for his business.

For starters, G Suite can help you use Gmail to send emails using your domain name instead of ‘gmail.com’ and have team conferences using Hangouts; and for the big enterprises, it could prove out to be one-stop cloud storage and management suite which also lets them create low-code applications for their business. The price for the basic subscription plan starts at $6 per user per month (for up to 30 GB Drive space) and goes up to $25 per user per month (for unlimited Drive space).

Other Google Cloud Products
G Suite, Maps API, and Translate API are a part of Google Cloud. Just like Amazon, the company also provides many other cloud-based products for developers and charge it according to the usage.
Revenue from Android And Play Store
Android doesn’t add revenue to Google’s pockets directly but it surely helps the company to save millions (or billions) of dollars which could have spent in the form of payments to other operating systems to keep Google as their default search engine and provide Google data to improve its advertising revenue model.
The brand, however, has smartly included freemium Google Play apps in every Android install. These Play Apps range from music to books to games and include a lot of things that can be bought and subscribed to on a smartphone.
Revenue From Wear OS
Wear OS is the operating system designed for the smartwatches. The revenue model of this OS is similar to Android as it comes with many preinstalled Google Apps.
Revenue From Google Chrome
Google Chrome was developed with a dire need to stop paying web browsers money to keep Google as their default search engine. It’s a free web browser which helps Google track your activities on the internet and use it for improving their performance and targeting ads.
Revenue From Devices (Made by Google)
It’s been three years since the company dived into the hardware devices market. Google makes and sells products include Pixel, Pixel Slate, Chromebook, Chromecast, Home, and Wifi. The company has capitalized on its existing brand image and has become a great competition to other players like Amazon, Apple, and Oneplus.
According to Android Authority, the company estimated a profit of $2.98 billion in 2018 with the majority of the profit coming from the brand Pixel ($1.78 billion).
Revenue From Google Domains
Google Domains is a domain registration service (currently in its beta stage) offered by Google. The company operates like any other domain registration service like Godaddy, NameCheap, etc. and even owns a top-level domain name – .dev.
Domain prices start at $12 per year.

Bottom-Line?
As you may have noted, the Google business model is huge and there are varied sources of revenue for the company. It has used its established brand image to expand its business model into domains and niches no one had even thought about before. Even the stated revenue sources above form just a part of the big business model. The actual revenue sources expand to other subsidiaries like Google AI, Google Ad Exchange, and other subsidiaries.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on how does Google make money | Google Business Model in the comments section.
Engineer by education. Writer by choice. I learn about new things by writing about them.






![AI Product Description Generator [Unlimited & No Login] Product Description Generator](https://www.feedough.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Cover-images-150x150.webp)


