The rapid development of technology has changed how the world works. User behaviour and media consumption has taken an entirely different route, thanks to the internet. This change has forced marketers to follow and adapt to the changing marketing channels. Even advertising isn’t limited to traditional channels anymore. It’s now the era of digital advertising.
Just like traditional advertising, digital advertising comes in numerous shapes, sizes, and forms. The basic principle behind digital ads is the same as that of conventional ads. Still, these ads have their own set of importance, types, advantages, disadvantages, and even operations that differ from traditional ads.
But what exactly is digital advertising?
What Is Digital Advertising?
Digital advertising is the action of calling public attention to an offering through online and digital paid channels by an identified sponsor.
Precisely, digital advertising is any form of advertising that appears online or on digital channels like websites, search engines, social media platforms, mobile apps, digital OOH, and other channels that can be accessed digitally.
Digital advertising is a branch of digital marketing and deals only with the promotional mix, and not with other Ps of the digital marketing mix.
Characteristics Of Digital Advertising
Digital advertisements come with their own unique set of characteristics. These are:
- Paid form: Digital advertising, just like other forms of advertising requires the advertiser (also called the sponsor) to pay to create the advertising message and creative, buy advertising space or slot, and monitor advertising efforts.
- Measurable: Digital ads are highly measurable in terms of how many people view them and how many people interact with them. Often, advertisers are even able to calculate accurate ROI of these ads.
- Goal-oriented: These ads are always backed by goals – to promote, sell, increase exposure, etc.
- Data backed: Digital ads are backed by data of what they are about, whom they are targeted at, and how the target audience interacts with them. Data forms the backbone of digital ads.
- Personal or non-personal: Ads on digital media can be highly personalised based on user activity over the internet or non-personal with a motive to enhance brand awareness.
Evolution Of Digital Advertising
The internet has changed the landscape of advertising. At the beginning of 90s, the investment in the digital advertisement was zero. But over the years, in 2025, digital advertising is expected to cross over $500 billion worldwide.

It all started in 1994 when hotwired.com, a Wired website, released the first banner ads on its website.

The same year saw the development of HTTP cookie that helped the advertiser and publisher track user behaviour.
Soon after, in 1996, Flash was introduced, which formed the framework for web advertising.
In 1997, pop-up ads were discovered and found wide usage all over the internet.
In 1998, Google launched and brought a concept of minimal search engines. The company started monetising in 2000 and paved the way for pay per click advertising and search engine marketing.
Mobile advertising also started in the year 2000.
In the early 2000s, Facebook launched and brought in its hyper-targeted ads model that used user interests and demographics for advertising. This started the trend of targeted ads.
The late 2000s and early 2010s saw the launch of YouTube, Smartphones, iPad, Instagram, Snapchat, Internet of Things, and Real-Time Bidding that later changed the advertising scenario to:
- Bidding
- In-app and mobile
- Microtargeting
The digital advertising agency is still growing, and everyday finds its application in a new channel.
Types Of Digital Advertising
The digital media landscape is vast. It caters to every activity of the user on a digital device and the web. Digital advertising makes sure to tap the user’s attention on every touchpoint it can. Thus, it can be divided into different types depending upon the type of ad, channel, and the ad’s intent.
Search Ads
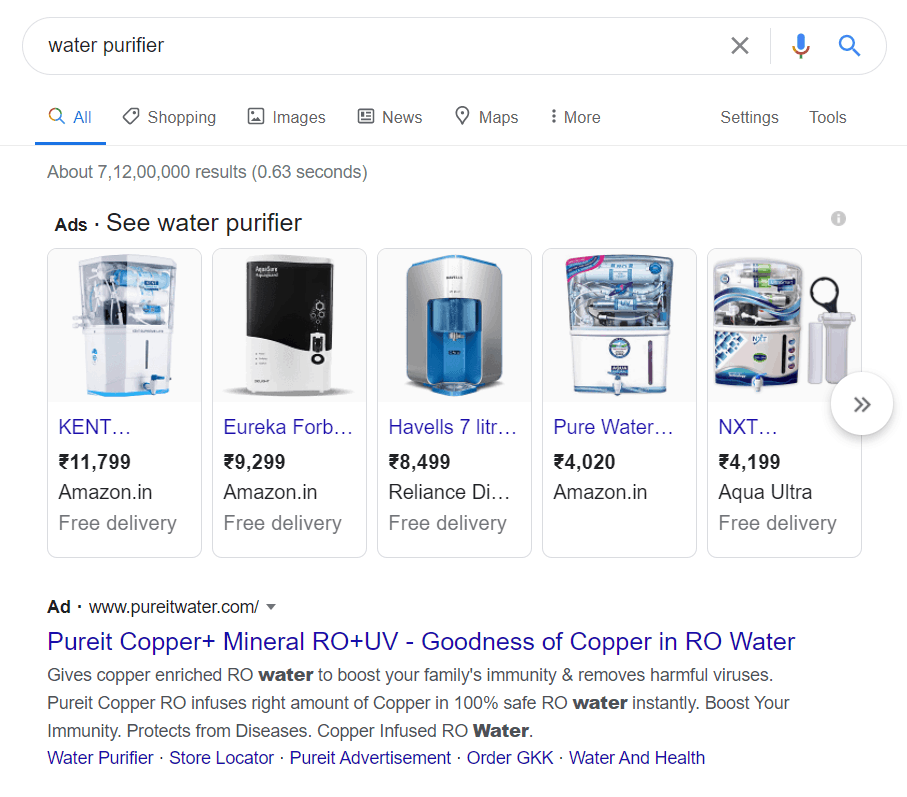
Also called search engine marketing, this type of advertising uses search engine results to promote the offering. Advertisers target keywords that people search for on a search engine and push their webpages at the top of the results by paying such search engines like Google, Bing, etc.
Such ad campaigns are intent oriented and are also called pay per click or PPC campaigns as they’re paid for by the advertiser only when a user clicks on the result.
These ads are further divided into search ads, shopping ads, maps ads, etc. depending upon the search engine they’re listed on and the intent behind the target user’s search.
Display Ads

Display advertising is the most common form of digital advertising. It comprises images, text, and animation, and shows up as banners on websites and blogs.
These ads can be personalised according to the user activity on the internet or non-personalised and are usually released to increase brand exposure, offer exposure, and fulfil other such motives.
Usually, display ads are further categorised as:
- Traditional Display Ads: These ads have fixed sizes and occupy a fixed space irrespective of the device the website is loaded on.
- Responsive Display Ads: These ads adapt to the size of the screen a website is viewed on.
Native Ads

Source: LinkedIn
Native ads are camouflaged ads that blend with the content they are added to. Sponsored listings within or after blog posts form an example of native ads. These ads result in better user interaction when compared to other forms of digital ads because of their property of matching the structure and function of the platform it appears on.
Video Ads
Video ads are digital ads used to promote an offering using videos or motion graphics that play before, during or after streaming content, or as a standalone banner or native ads.
Used mostly on video streaming platforms like YouTube, Facebook Watch, etc. video ads are also used on websites and blogs as out-stream ads to gain website users’ attention.
Audio Ads
Audio ads are used majorly on audio streaming platforms like Spotify, LiveXLive, Pandora, etc. The advertiser gets into a contract of the streaming platform or the content creator to add the brand’s ads within, before, or after the content.
Mobile Ads

Mobile ads are digital ads that are delivered on mobile devices. These ads use two different platforms:
- Mobile Web: These are the websites, blogs, and webpages arranged to fit the mobile screen sizes.
- In-App: Mobile applications are specialised applications developed to target specialised moments. These apps are easy to download, navigate, and involve a higher retention rate than other channels.
Remarketing Ads

Remarketing ads are digital ads targeted to a brand’s online visitors with a motive to bring them back on the website or application, or perform an action. For example, a brand targeting its ecommerce store’s visitor through ads to make him complete his/her incomplete transaction. Another example could be of an event brand that targets its website visitors with informative ads of new events that they could attend.
Social Media Ads

Social media ads appear on social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat, Reddit, LinkedIn, etc. These ads can be display ads, native ads, video ads, audio ads, remarketing ads or mobile ads.
Social ads are hyper-targeted ads that target the users depending upon their demographics, locations, interests, and even psychographic and behavioural interests.
Influencer And Curator Ads
Influencer ads and curator ads are comparatively new ad forms where a brand directly contacts the content developers and/or content curators with good followership to place the brand or offering in their content. This helps the brand to gain exposure and trust of the influencer’s followers.
How Does Digital Advertising Work?
Even though digital advertising is different from traditional advertising, it works in a way similar to the latter. There are parties involved, a contract backs the transaction, and the creative and the ad copy is developed to meet the advertising goals.
Parties
A typical digital advertisement involves three different parties:
- Advertiser: It’s the brand that creates and funds the advertisement. For example, Nike with its campaign ‘Just Do It’.
- Advertising Network: It’s the middleman that connects the advertiser with the publishers and the advertisement space providers. For example, Google runs AdWords for advertisers and AdSense for publishers.
- Publisher: A publisher is anyone who owns a digital property and is willing to monetise that property by selling ad spaces. For example, Feedough.com.
Generally, an advertising network acts as a mediator that connects an advertiser with numerous publishers or digital property owners.
However, in cases of big players like with social media advertisements, the publisher, like Facebook, LinkedIn, etc., becomes the advertising network itself.
Structure
Every digital advertisement is backed by a goal or a motive. It could be to get more exposure, more leads, remarketing, or more action performed. And this goal forms the spine on which the advertisement’s structure stands on.
Besides the goal, the advertisement structure includes the following:
- Medium: Which medium will the ad use to reach out to the users?
- Creative: What will be the graphic and textual content of the ad creative?
- KPI: How will the advertiser measure the return on investment for the advertisement campaign?
Contract
A variety of contract models exist for digital advertising. These are:
- Pay Per Impression (PPI): The advertiser pays a fee every time an ad is displayed to the user, no matter if an action is performed over the ad or not.
- Pay Per Click (PPC): The advertiser pays a fee every time an ad is clicked on.
- Pay Per Action (PPA): The advertiser pays a fee every time the user performs an agreed action. The action could be anything from filling up a form, signing up, registering for something, or buying a product.
Generally, more than one advertiser applies for a single ad space which increases the competition. Space is then provided to the advertiser who bids the most. This process works real-time and is called real-time bidding.
Digital Advertising Vs Traditional Advertising
Traditional advertising is offline advertising. It involves using channels like magazine, newspaper, television, radio, direct mail and billboards to advertise an offering or an idea. These ads differ considerably from digital advertising.
Digital Advertising | Traditional Advertising | |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Digital advertising is the act of calling public attention to an offering or an idea through online and digital paid channels by an identified sponsor. | Traditional Advertising is the act of calling public attention to an offering or an idea through offline paid channels by an identified sponsor. |
Medium | Online and digital channels like website, search engines, social media platforms, etc. | Offline channels like radio, television, newspaper, etc. |
Data-Driven | Digital ads development, deployment, and measurement are backed by data. | It isn’t possible to get accurate data to back all traditional advertisements. |
Communication | Digital ads include both single sided communication and two-sided communication. The user gets to interact with the advertisement. | There’s no way for a user to interact with a traditional advertisement. |
Pros And Cons Of Digital Advertising
Digital advertising comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages that sets it apart from traditional advertising.
Advantages
- User-Targeted: Digital advertising is highly user-targeted and can even be microtargeted to the target audience’s smallest section.
- Inexpensive: Considering the ROI of digital ads, it is considered an inexpensive form of promotion.
- Data-Backed: Digital ads are data-backed. This data can be used to develop campaigns that were not possible before.
- Interactive: Digital ads can be made interactive, increasing engagement and proving beneficial for both the advertiser and users.
- Real-Time: Changes in digital ads can be made real-time. Even the analytics and data can be collected in real-time. This proves to be a great advantage.
- Global Coverage: It’s easy to launch digital ads to a worldwide audience without even going to such places.
- Wide Range Of Formats: Digital ads come in numerous shapes and sizes, and the scope is still untapped.
Disadvantages
- Limited Audience: Only 59 percent of the global population uses the internet. The rest don’t have access to it yet. So, if the brand’s target audience doesn’t have internet access, digital advertising could be of no use.
- Competition: Many advertisers bid for one ad space that increases the competition and prices of ads.
- Increasing Ad-Blockers: Ads are everywhere. This bugs digital users who look for ways to block such ads.
- Requires A Specialised Skillset: Running digital ads requires a specialised skill set to develop and optimise ads and bidding for the same.
Digital Advertising Examples
Here are some examples of each type of digital advertising to understand the concept better.
Search Engine Marketing
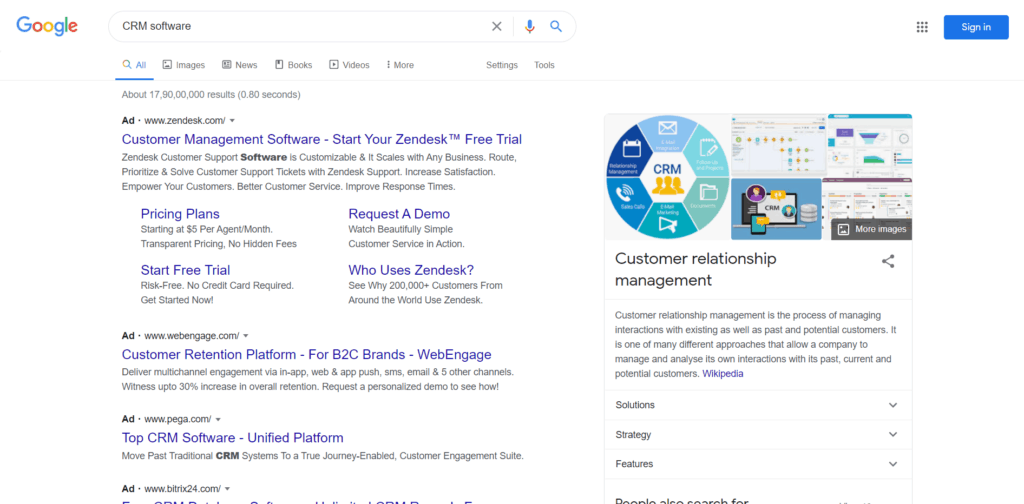
Search engine ads usually appear as native ads on search engines like Google. Such ads appear at the top of the results and are prefixed with the term ‘Ad’.
Display Ads

Display ads occupy a particular space on publisher’s digital property in return for money.
Social Media Ads

Social media ads usually appear as native ads on social media channels like Facebook, Linkedin, etc. However, these ads do carry a tag of ‘ad’ or ‘sponsored’ on them.
Mobile Ads

Mobile ads are specific to mobile websites and apps. These ads are developed in sizes that cater mainly to the mobile audience.
Video Ads
Video ads are usually developed to promote to video consumers before, after, or in their video.
Remarketing Ads

Remarketing ads are tailor-made ads including offers and other CTAs designed especially for the users who visited a particular website or webpage.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on digital advertising in the comments section.
A startup consultant, digital marketer, traveller, and philomath. Aashish has worked with over 20 startups and successfully helped them ideate, raise money, and succeed. When not working, he can be found hiking, camping, and stargazing.









