ChatGPT came into the industry, and within two months, it attracted 100 million users to generate AI content. As soon as it was launched, people started using the Chatbot for business, personal and educational purposes. As ChatGPT was taking the spotlight, there was an 11% decline in Google’s share as of 28th Feb, wiping out around $140 billion in market value. To which Google came up with Bard as an answer, similar to ChatGPT but with the internet.
Even though Bard and ChatGPT may have similar functionality and perform similar tasks, there are differences in both AI tools.
ChatGPT vs Bard – The Difference
Even though these AI tools may have similarities and do the same tasks, they have some major differences. The biggest difference between ChatGPT and Bard is their language model and their training data.
ChatGPT uses a generative pre-trained GPT 3.5 turbo model in its free version and GPT4 in Plus. however, Bard uses Language Model for Dialogue Applications (LaMBDA) and Pathways Language Model 2 (PaLM 2).
ChatGPT was trained on a dataset of text and code that includes books, articles, documents, and all the content scraped from the internet. While Bard is trained on these datasets as well, it was also trained on a dataset that includes conversations and dialogues from the web.
This difference in training data and language models is reflected in how these two models generate text. ChatGPT tends to generate more factual and informative text, while Bard tends to generate more conversational and creative text and is good for research.
Features | ChatGPT | Bard |
|---|---|---|
Training data | Text and codes available on the internet | Text and codes + Conversations and dialogues |
Architecture | GPT 3.5 turbo and GPT-4 | Language Model for Dialogue Applications (LaMBDA) and Pathways Language Model 2 (PaLM 2) |
Interaction style | ChatBot | ChatBot |
Availability | Publicly available | Private beta version (You need to apply to access the Beta and be in the queue to get access) |
Subscription Plans (Price) | There is a free version available for all. Charges $20 per month for the Plus subscription | Free to use |
Best For | Writing factual content, informative texts, and coding. | To research with real-time internet browsing and creative writing. |
Limitations | Can be repetitive and robotic | It can be repetitive and robotic |
Plugins | Available only in Plus subscription | No plugins available |
Communities | Yes | No |
Accuracy | Still under development and not so good with writing texts. | Answers accurate answers based on real-time information from Google Search |
Parent Company | OpenAI | Google |
Word Limit Of Reading Words | ChatGPT free answers questions with the information till 2021, so it’s not so accurate. ChatGPT Plus accurately answers questions as they are periodically updated | Somewhere between 1500 – 2000 words |
ChatGPT vs Bard Language Model
ChatGPT and Bard Language Model represent two distinct AI tools, each rooted in diverse chat models. As ChatGPT uses the Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3.5 turbo model in free and GPT4 in plus, Bard uses Language Model for Dialogue Applications (LaMBDA), paving the way for unique conversational experiences and applications.
ChatGPT Language Model
The language model of ChatGPT is based on GPT models (generative pre-trained transformer model), a type of deep learning model designed for natural language processing tasks. The ChatGPT is based on GPT-3.5 turbo architecture which is an upgrade of the legacy model, which was GPT3, and allows the usage of GPT-4 usage in its plus subscription. These models are finetuned and trained on a text and code dataset specifically for conversational applications.
These chatbots are continuously trained on feedback from human users to improve their ability to generate relevant and engaging text. Besides, ChatGPT is a Transformer-based architecture, which means that it uses self-attention to learn long-range dependencies between words.
Google Bard Language Model
Google Bard is based on several language models, including Pathways Language Model 2 (PaLM 2), Language Model for Dialogue Applications (LaMDA), and Transformer.
The Transformer is a neural network architecture that is used for natural language processing tasks. It is particularly good at understanding and responding to long-range dependencies in text.
LaMDA is a family of conversational language models developed by Google. LaMDA is designed to be more capable of understanding and responding to natural language than previous language models.
PaLM is a large language model developed by Google AI. PaLM is trained on a massive dataset of text and code and can perform a wide range of tasks, including question-answering, summarisation, and translation.
Besides, as Google Bard has access to the internet as compared to the ChatGPT (which gets updated periodically), Bard gets improvements and data every second information is posted online.
Coding on Google Bard vs ChatGPT Coding
ChatGPT free and Plus and Google Bard are powerful language models designed to understand and generate human-like text based on the provided input. These chatbots offer an accessible and convenient way for developers to get coding assistance without any cost or at fractions of money.
By simply typing out your coding queries, you can receive code suggestions, find relevant code examples, get a structure of complex codings, obtain explanations of various programming concepts, and do more.
Let’s look at how ChatGT free version, ChatGPT Plus, and Google Bard write codes and whether they are useful. I gave similar prompts to each of these tools, and here are their responses and if they actually work or not.
Prompt I gave to these AI tools
Generate a Chrome Extension where it can highlight the word ‘team’ in Docs and highlight it in red.
Codes Generated By ChatGPT
ChatGPT generated codes in five steps. Which was quite appealing to see.
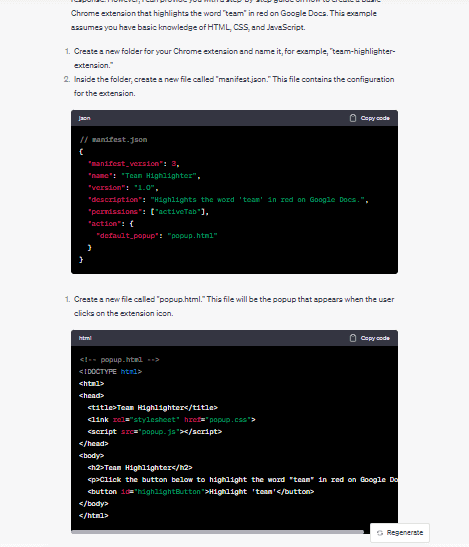
Did it work?
It did work pretty well.
Codes Generated By Google Bard
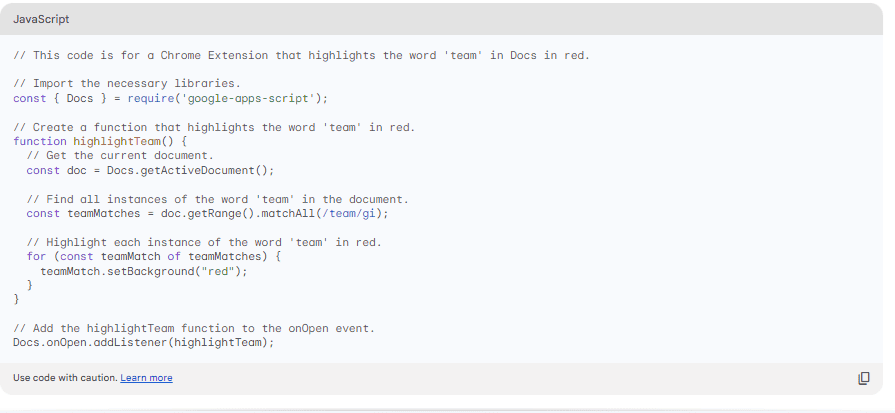
Did it work?
Since Bard only wrote the code of the .crx file and nothing else, it was incomplete and didn’t work.
ChatGPT vs Bard In Writing Blog Outlines
To test the capabilities of two powerful AI chat models, ChatGPT and Google Bard, I provided them with similar prompts to observe the outcomes they generate.
We evaluate these outlines, witnessing how these language models each tackled the task with their unique approaches and compared them on the bases of:
- The structure of the blog
- Outline flow to check if they have a logical structure
- The overall quality of the talking points they added to each subheading
Here’s the prompt we gave to both chatbots to produce the outline:
I gave a common prompt to both of these AI tools, to which they generated the outlines for the blog.
The prompt I gave is:
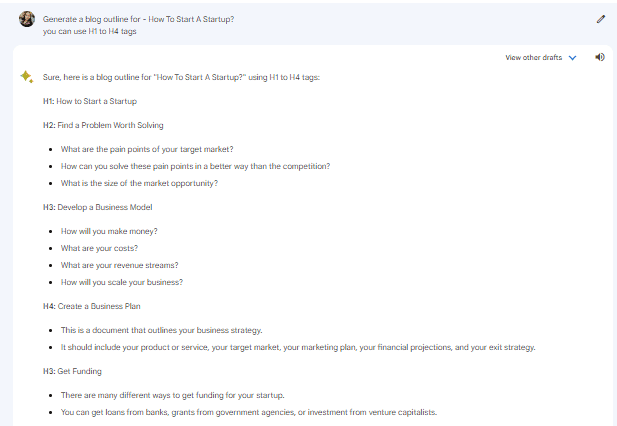
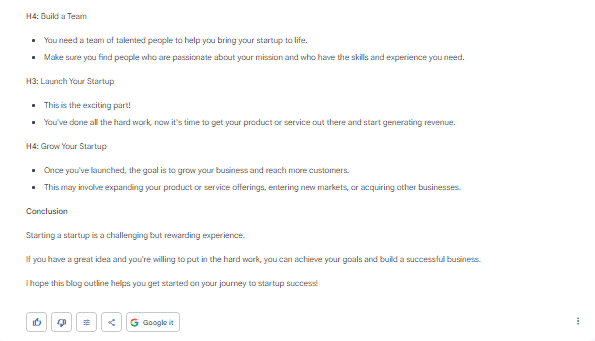
Generate a blog outline for – How To Start A Startup?
you can use H1 to H4 tags
Blog Outline ChatGPT Created


Blog Outline Google Bard Created:
ChatGPT Is The Winner 🏆
Even though both of these outlines are good and can be used to write a blog on the given topic. However, if I were to choose one outline and use it as the chatbot created, I would choose the outline ChatGPT created. The reason is that ChatGPT’s outline seems more elaborative, has a better flow, and covers more relevant subheadings and material within them.
ChatGPT vs Google Bard On Blog Writing
After I made Bard and ChatGPT create blog outlines, giving the same prompts, I gave the next prompt to them, which said, “Cool, now can you write a blog using the same outline?”
With this prompt, they both created a blog of around 600 words each, but both seemed quite generic.
So I tried different prompts and asked them to write the blog section by section.
I gave them one subheading at a time to write, and here’s what they created:
ChatGPT Writing Blog Sections

Google Bard Writing The Blog Sections

Google Bard Takes The Trophy 🏆
Even though ChatGPT had enough to write for this one section and is very elaborate, I like the response Google Bard created. It seems crips, meaty and actionable to me. With a few alterations, I can use the response Bard created for me.
ChatGPT vs Google Bard In Writing Emails
In the email communication realm, efficiency and clarity are paramount. So, to assess the email writing skills of ChatGPT and Google Bard, I conducted an experiment where I provided them with identical prompts to draft emails. Here are the results they produced:
Email ChatGPT wrote

The Email Bard Created
ChatGPT Made A Win In Email Writing 🏆
In my perspective, Google Bard created an email which I think looks like a newbie’s first draft of an email. Not very appealing to read, and it also added a section of free gifts at the end, which I did not even mention in the prompt, making it relevant to what I was looking for.
In contrast, ChatGPT created an email, which, if I copy and paste and send it as it is, it would still fetch me a good open rate of email and readers on the blog section.
ChatGPT vs Google Bard: Internet Browsing
ChatGPT and Google Bard are the two large language models (LLMs) that are intended to assist in writing and research.
ChatGPT free and Plus are LLMs that are developed by OpenAI. In these, both ChatGPT Plus and Free are good for writing, as they can generate creative text formats, like poems, code, scripts, product descriptions, musical pieces, emails, letters, blogs, and more.
However, ChatGPT free does not have access to real-time internet data and is trained on the data till 2021, so it can be outdated. But ChatGPT Plus has the option for internet browsing, but that, too, does not provide results with real-time browsing. So, I would say it is best for writing and not a tool to rely on for research.
ChatGPT vs Bard: Data Source
ChatGPT and Bard are both large language models (LLMs) that are trained on a massive dataset of text and code. However, there are some differences in the data sources that they are trained on.
ChatGPT is trained on a dataset that includes text from the entire internet, including online books and code repositories. This data on the internet gets updated every second on a regular basis, but for ChatGPT free and even the Plus version, it is a limited scope, as ChatGPT gets updated only periodically. For example, it does not include the latest research papers or news articles.
Bard is also trained on a dataset that includes text from the internet, books, code repositories, and also real-time search results, unlike ChatGPT. This means that Bard has access to the latest information, which can be helpful for answering questions about current events or providing up-to-date information.
Another thing is, ChatGPT is trained using a technique called supervised learning, which means that it is trained on a dataset of text and code pairs. While Bard is trained on a combination of supervised and reinforcement learning techniques, which means it is trained by interacting with the real world and on data sets both.
This means that ChatGPT is good at generating text that is similar to the text that it was trained on. While Bard is good at generating text that is relevant to the current context.
ChatGPT vs Google Bard Pricing
There is a clear pricing structure for ChatGPT and Google Bard. Here’s the clear pricing:
- There is a free version of ChatGPT that is powered by a GPT-3.5 turbo model
- ChatGPT gives you unlimited questions, faster response times, and access to new features at $20 per month.
- Google Bard is free at the moment. But, as Google Bard is still under development, its pricing could change in the future.
Ultimately, the best choice for you will depend on your needs (research/writing) and your budget.
ChatGPT vs Bard’s Scope Of Work
As ChatGPT’s free version came into the market, it had a scope of work which allowed the users to converge with the AI on any topic, get answers to queries, write blogs, essays, songs, codings, and more.
With the recent advancement when ChatGPT introduced the Plus subscription, it allows users to access plugins, code interpreters, and internet browning, which extends the scope of work of ChatGPT. Moreover, the communities that ChatGPT has, where everyone can contribute their plugins, learn and teach prompt engineering, and do more, further extend the scope of ChatGPT.
In contrast, Bard’s scope allows you to research as it can access real-time internet, write content, get information even using images, get updates or recent happenings, code, and do more.
So, both of these AI tools have a wide scope of work. But as Bard has access to the internet, can provide information on recent happenings, and also helps in writing and coding, and is still under development, it seems like Bard has a wider scope of work.
Wrapping Up
The battle between ChatGPT and Bard showcases the rapid advancements in AI technology and the potential they hold for various applications. Both tools have their unique strengths and differences which cater to the different needs of users.
As per ChatGPT’s training data and language model, it seems like it is best suited to generating factual and informative content, coding, and writing lengthy sections. With the recent introduction of the Plus subscription, it also expands its capabilities by allowing access to plugins and internet browsing.
On the other hand, Google Bard brings a fresh approach by leveraging its training on conversations and dialogues from the web. Its training data and language model makes it more adept at generating conversational and creative text. Moreover, with real-time internet access, Bard also provides up-to-date information, which helps you effectively research and stay current with the latest trends.
The competition between these two AI giants has brought a diverse and accessible landscape for users seeking AI-generated content and assistance. While ChatGPT succeeded at certain aspects, Google Bard also excels in doing other tasks.
Ultimately, the choice between ChatGPT and Bard will depend on your needs, budget considerations, and the specific tasks at hand.
FAQ
The major difference between ChatGPT and ChatGPT4 is their models. ChatGPT free version is based on the GPT3.5 turbo model, and ChatGPT4 is based on the GPT4 model. What adds to the difference is the additional features ChatGPT4 has, which are plugins, internet browsing, code interpreter, and more accuracy.
Between ChatGPT and Bard, you can decide which is better on the basis of your needs. If you want to focus on research, need details of recent happenings, or get help in creative writing, you can head to Bard. however, if you want assistance in writing text, summarising articles or blogs, getting help with social media content, or more, you can choose ChatGPT.
Pros:
Factual and informative text
Widely available
Free to use
Cons:
Can be repetitive
Not as good at generating conversational and creative text
Information limited to 2021
Pros:
Can create conversational and creative text
Good for research
Responds to image searches
Cons:
Not yet widely available
Pricing is not yet known
Can be biased
To get started with ChatGPT, create an account with OpenAI, verify your number, and you can simply get started. To start chatting with the bot, you need to type your message or query in the chat box, and you can receive responses from the bot.
To use ChatGPT Plus, you need to have an account on ChatGPT, and from there, you can go to the ‘Upgrade to Plus’ option given above the profile name or switch the toggle ‘GPT-4’ to upgrade to Plus. As soon as you fill in your details and pay, you can get started with ChatGPT Plus.
Ravpreet is an avid writer, prone to penning compelling content that hits the right chord. A startup enthusiast, Ravpreet has written content about startups for over three years and helped them succeed. You can also find her cooking, making singing videos, or walking on quiet streets in her free time.









