Products have similar lives to living beings. They are born someday and they come to an end someday. Product life cycle is the set of stages a product goes through during its lifetime. The journey starts from the day it is just an idea to the day it is finally removed from the market.
Usually, there are 4 different stages in the Product life cycle.
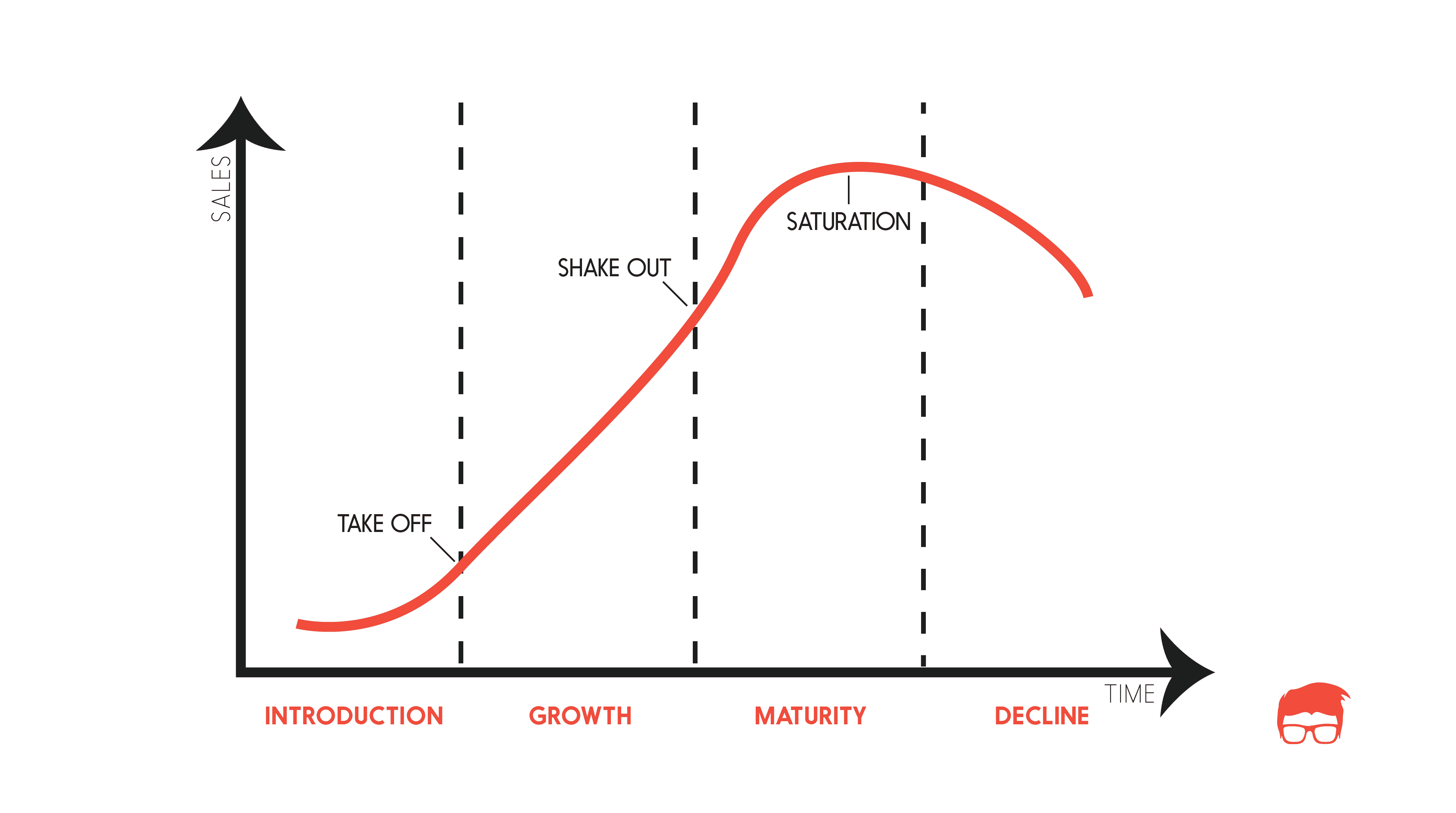
Introduction Stage
This stage is where the idea becomes an actual product for sale in the market. A product is introduced to the market during the introduction stage. There are many features of this stage of product life cycle:
- Small Market: This stage involves business capturing the market. Every customer is the new customer. Sales are less.
- Buzz: This stage involves creating a buzz. A buzz about the new brand is created in the market and the potential customers and competitors get to know about the product. Many companies start to promote their product even before the introduction stage but such promotions may backfire as the competitors get time to adjust accordingly.
- High Costs: There are no economies of scale in the introductory stage as the demand is yet to be created. This high production cost combined with distribution and marketing and promotion costs are high for the start.
- Less/No Profits: Since the demand is yet to be created, the business starts off with a loss.
Marketing Mix in the Introductory Stage
Product
Introductory stage of the product life cycle involves establishing a brand and executing the positioning strategies. It also involves obtaining intellectual property protection like patents and trademarks.
Price
Price mix is decided based on the product, the competition in the market, and the future revenue generation strategies.
- Penetration pricing – starting with a low introductory price to attract and keep the market share. Start low increase later.
- Price skimming – keeping the price high initially if the product is unique and the company can charge a high price for it.
- Competition Pricing – choosing the price as it is already prevalent in the market. Competition decides the price.
Place
This depends on the size of the company. Usually, the distribution is kept selective and scattered, to learn about what market likes and what not.
Promotion
More focus is on brand awareness. Free samples may be distributed. Investments are done on advertisements and digital marketing. Brands try to engage as many people as possible. The main focus is to create more and more demand through promotion.
Growth Stage
A product finds its place in the market at the growth stage. This stage is characterized by increased sales and revenue. Profits also improve as the company gets a benefit of economies of scale with the rise in customer demand.
Following features can be seen in the growth stage of product life cycle.
- Awareness: The Company has already worked on creating a brand awareness in the introductory stage and the customers are more aware of the brand.
- Increased Sales: Growth stage witness customers repeating the purchases. They might have already set the product as a preference in this growth stage. This increases the sales of the sales.
- Low costs: Increased sales results in more demand for the product. More demand means more production, which results in the company getting the benefit of economies of scale.
- Increased Competition: The increased popularity of the brand results in an increase in the competition in the market.
- Marketing techniques: Growth stage witnesses a change in marketing focus of the companies. They now spend more resources on increasing brand equity and brand preference. More money is spent on advertising, digital content and public relations so as to engage the customers for long.
Marketing Mix in the Growth Stage
Product
The depth of product line may increase. That is, different variants of the same product may emerge during the growth stage. Product quality improves. Packing and new features are added.
Price
Different pricing strategies executed during the introductory stage are revised.
- Penetration pricing – customer base is set, the company now can increase the prices or reduce the discount offered.
- Price skimming – by this time, competitors start appearing in the market and prices could be lowered if competitors start capturing the current customer base of the company.
- Competitive prices – prices usually depend on the prices of the competitor’s product.
Place
Distribution becomes more intensive. More trade channels are added to increase supply in the market. The business now tries to tap more markets.
Promotion
The introductory stage has already helped the business in creating a brand. The main focus of marketers during growth stage is to increase the brand equity.
Maturity Stage
Maturity stage is when sales are at their peak and grow at a slower pace. Competitors’ product becomes more similar and it becomes hard to retain the market share during the maturity stage. Hence, the company starts more aggressive practices of lowering the price, sales promotion, adding more product lines, modifying existing product lines, opening up new distribution channels and rewarding the existing channels.
The maturity stage of product life cycle has the following characteristics.
- Most Profitable: Sales are at the peak at this stage. Hence business earns maximum profits.
- Increased Competition: The increase in demand for the product increases the number of competitors in the market.
- Less Market Share: The demand for the product divides as product differentiation decreases among the competitors’ products.
- Product Innovation: The company comes up with different ideas to differentiate its product from the competition. This result in innovation as new ideas for production, pricing, placing and promotion emerge.
- Decrease in Price: Increased competition may force the company to decrease the price of the product.
- Decrease in Profits: A peak is always followed by a fall. Hence, profits start to decrease eventually.
- Marketing Strategies: Marketing focus shifts to more of sale promotion and direct selling. Businesses focus more on capturing the competitors’ market share by making customers more brand loyal. Incentives are also provided to sellers to increase the shelf space of the product.
The maturity stage can turn out to be the introductory stage for various new product lines.
Marketing Mix in the Maturity Stage
Product
Maturity stage witnesses the most innovation. New features are added to the same product to differentiate it from the competition. New product lines may also emerge if the company sees the fall of the product in the near future. Product width increases in the maturity stage of the product life cycle.
Price
This stage involves lowering of the prices as competition increases and business aims to maintain its market share.
Place
More distribution channels are looked at. Businesses start to pay more for more shelf space. It also starts to give more margins to the sellers to increase the sale.
Promotion
More emphasis on building up of brand loyalty and brand preference. Focus shifts to sale promotion and direct selling. The business focuses more on capturing competitors’ market share.
Decline stage
A peak is always followed by a fall. Technological obsolescence, change in customer tastes, market demand saturation, or introduction of a new better substitute etc. can lead to the decline of the existing product. This stage is the beginning of the end of the product.
Decline stage of product life cycle has following characteristics
- Market decline: This stage sees a fall in market demand of the product which results in a decrease in sales and decrease in profits, eventually.
- Falling Prices: In hope of maintaining intact the demand for the product, the company decides to decrease its price.
- Few Options: Very few options are left with the company during the decline stage. It either
- Withdraw the product from the market.
- Try to incorporate innovation, or
- Wait for competitors to exit.
Marketing mix in the Decline Stage
Product
Some products in the product line may be discontinued, while others are altered. The company focuses on innovative strategies to stay in the market.
Price
Prices may be lowered to sell off the remaining inventory of the discontinued products. Other products may also see a fall in price as the company has to maintain competitive pricing.
Place
Selective distribution. Distribution is done only in places with sure shot demand. Trade channels may be reduced.
Promotion
The main focus is on the brand image as new products are planned to be introduced. Promotion budget on existing products is reduced. More focus on public relations and publicity.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think of this article on Product Life Cycle in the comments section.
A startup consultant, digital marketer, traveller, and philomath. Aashish has worked with over 20 startups and successfully helped them ideate, raise money, and succeed. When not working, he can be found hiking, camping, and stargazing.