If you had asked me about some examples of AI a decade ago, all I would have had were speculations, but today, AI is everywhere. From helping you with trivial tasks like writing an email to driving a car, AI has revolutionised our lives in ways we couldn’t even imagine.
While ChatGPT made the masses aware of AI’s potential, there are numerous other real-world examples of AI applications that have already entered our daily lives. Let’s take a look at some of them.
But first, for beginners, what exactly is AI, and how does it work?
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, refers to a technology that enables machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, like problem-solving, learning, and decision-making.
This technology is about making machines smart. It involves programming computers to do things that usually need human thinking, like understanding speech, recognising images, or making decisions.
For example, when you ask Siri or Alexa a question, they use AI to understand your words and provide a helpful response.
AI systems are powered by a combination of algorithms and data. They learn from the data they are fed and can improve their performance over time, just like humans.
Examples Of AI In Everyday Life
We encounter AI in our daily lives, often without even realising it. Here are some common examples of AI applications that have become an integral part of our routines:
- Virtual Personal Assistants: Virtual personal assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant use AI to understand and respond to our voice commands. These assistants can perform various tasks like setting alarms, making calls, or even ordering food.
- Social Media Algorithms: Social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram use AI algorithms to personalise our newsfeeds and show us the most relevant content. These algorithms analyse our behaviour, preferences, and interactions on the platform to curate a feed that keeps us engaged.
- Online Shopping: E-commerce platforms like Amazon use AI to recommend products based on our browsing history and purchase behaviour. This personalised recommendation system uses machine learning algorithms to understand our preferences and show us products we will most likely buy.
- Facial Recognition: Smartphones and other devices use AI-powered facial recognition technology to unlock our devices or make payments. This technology learns and improves over time, making it a convenient and secure way of identification.
- Navigation Systems: Navigation systems like Google Maps or Waze use AI-powered location data and real-time traffic updates to provide the best route for our destination.
- Fraud Detection: AI is also used in fraud detection systems to analyse patterns and anomalies in financial transactions. This helps banks and financial institutions to detect and prevent fraudulent activities.
- Smart Home Devices: Various home devices use AI for automation and convenience, from smart thermostats that adjust the temperature according to our preferences to smart lights that turn on or off based on our presence.
AI In Different Industries
From changing how cars are driven to revolutionising healthcare, AI is entering various industries. Let’s explore some of the areas where AI is being used:
AI In Healthcare

AI is transforming healthcare by helping doctors diagnose, plan treatment, and develop drugs.
AI algorithms can quickly and accurately analyse medical images, such as MRI scans, X-rays, and CT scans, to detect anomalies and assist radiologists in making diagnoses.
For example, Viz.ai has developed a technology that uses AI to identify critical conditions like strokes from brain scans, allowing doctors to intervene quickly and reduce disability and mortality.
AI even aids drug development by predicting the efficacy of new drugs and identifying potential side effects, reducing the time and cost of clinical trials. For example, In 2020, BenevolentAI used its AI platform to identify Eli Lilly’s rheumatoid arthritis drug Olumiant as a potential COVID-19 treatment. It received FDA emergency authorisation in just 3 days.
Example Of AI In Healthcare: IBM Watson Health

IBM Watson Health uses AI to analyse medical literature, clinical trial data, and patient records to provide insights for personalised treatment plans, improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment recommendations.
Clinical Decision Support
IBM Watson Health provides clinical decision support tools that help healthcare professionals make more informed decisions. For example, Watson for Oncology analyses patient medical records and the latest research and clinical guidelines to provide evidence-based treatment recommendations for different cancer types.
AI-Powered Chatbots
IBM Watson Health employs AI-powered chatbots to assist patients with their healthcare needs, providing personalised information and support even outside regular business hours. These chatbots can also help schedule appointments and refill prescriptions, freeing medical staff to focus on more complex issues.
AI In Legal Industry

The legal industry has adopted AI to automate routine tasks, enhance legal research, and streamline operations. AI-powered tools can analyse large volumes of legal documents and contracts, identify patterns, and predict outcomes. This helps lawyers save time on mundane tasks and focus on complex legal issues.
Some lawyers are also employing legal AI chatbots to interact with clients and provide legal advice. These chatbots are trained using natural language processing (NLP) techniques, allowing them to understand and respond to complex legal queries in a human-like manner.
AI-powered tools today also assist lawyers with legal research, helping them find relevant case laws and statutes quickly. This not only saves time but also improves the accuracy of legal work.
Example Of AI In The Legal Industry: Kira Systems
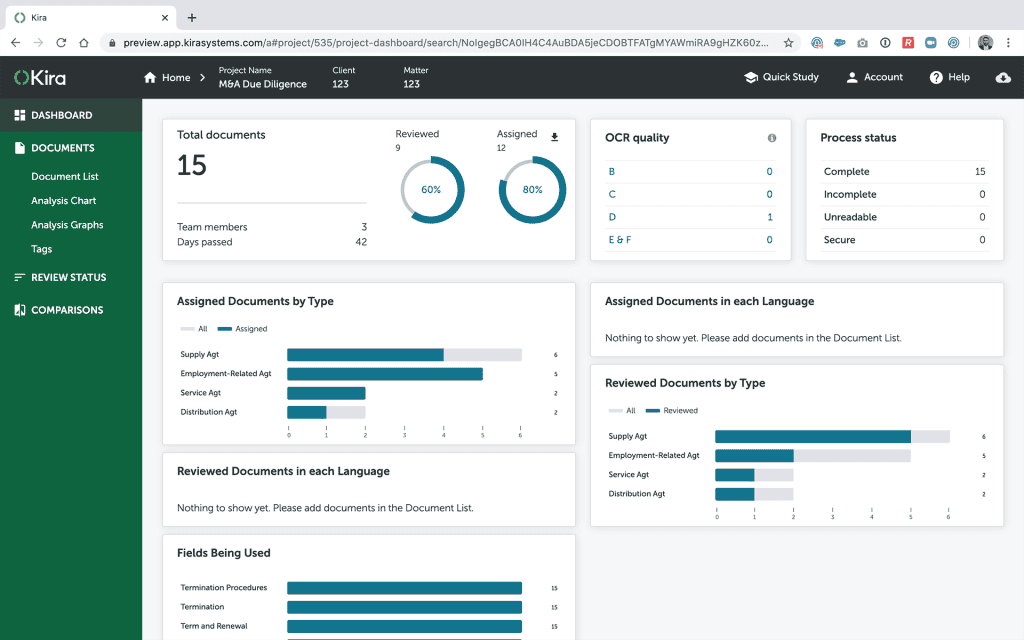
Kira Systems is an AI-powered contract analysis tool that quickly and accurately identifies relevant clauses in legal documents. It can extract data from various types of contracts, such as NDAs, leases, and employment agreements, saving lawyers hours of manual review.
For example, a lawyer can use Kira Systems to review an entire merger agreement and identify key clauses related to indemnification, representation and warranties, and closing conditions. The tool is trained to complete the task with high accuracy in a fraction of the time it takes a human to do it.
Here’s how Kira Systems leverages AI to improve efficiency and accuracy in contract review:
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP refers to machines’ ability to understand and process human language. It is how an AI-powered tool can read and analyse legal documents just like a human lawyer would.
Kira uses advanced NLP algorithms to understand and interpret the language and context within legal documents. This allows it to accurately identify, extract and analyse key information like parties, dates, obligations, limitations, etc.
Machine Learning
Machine learning refers to the ability of a machine or software to learn and improve from data without being explicitly programmed.
Kira’s patented machine learning technology enables it to learn from examples of provisions and clauses provided by experienced lawyers. It builds probabilistic models to recognise relevant language patterns.
AI In Ecommerce
The ecommerce industry has seen a significant rise in the use of AI-powered tools and technologies over the past few years. With the increasing volume of online transactions and data, AI offers a valuable solution for streamlining processes and improving customer experience. Here are some ways AI is being used in e-commerce:
- Personalisation: Big e-commerce companies like Amazon and Alibaba use AI algorithms to analyse customer data and provide personalised product recommendations. These algorithms consider factors like browsing history, purchase history, and even social media activity to suggest products that the customer is most likely to be interested in.
- Chatbots: Almost every e-commerce website now has a chatbot feature that uses AI to provide customer support and assistance. The platforms feed these chatbots with vast amounts of data, allowing them to understand and respond to customer queries quickly and accurately.
- Supply Chain Management: AI-powered tools can analyse demand and supply data to predict inventory requirements, optimise logistics, and reduce fulfilment time for e-commerce companies. This helps businesses save on shipping costs and improve overall efficiency.
- Pricing Optimisation: Since AI can analyse vast amounts of data and predict market trends, it is being used to optimise product pricing in real time. This helps e-commerce businesses stay competitive and maximise profits.
Example Of AI In Ecommerce: Sephora
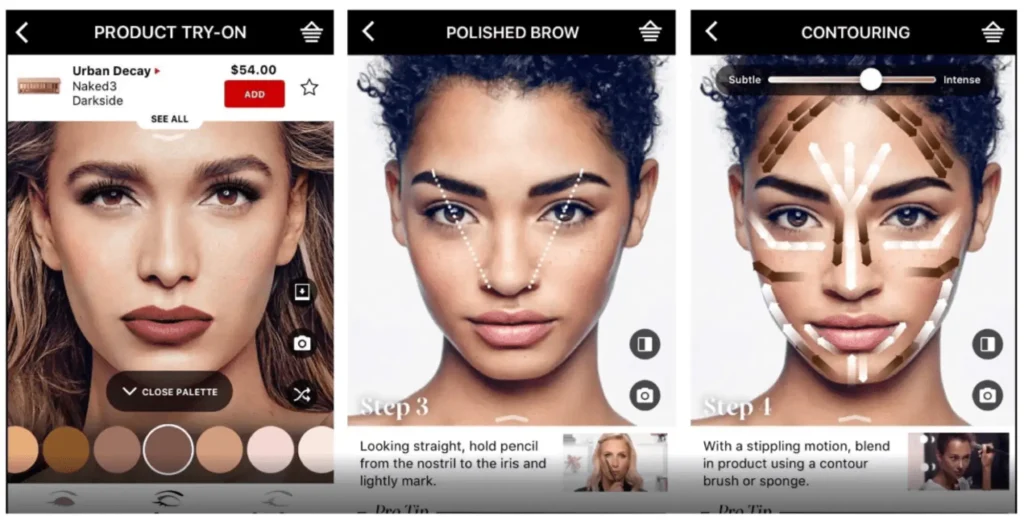
Sephora is a leading beauty retailer known for its wide range of cosmetic and skincare products. They have been at the forefront of using AI in their e-commerce platform to enhance the customer experience. Here’s how they’re doing it:
- Visual Search and Virtual Try-On: Sephora’s Visual Artist feature uses AI-powered facial recognition to allow customers to try on thousands of shades of lipstick, eyeshadow, and other cosmetics virtually. The Visual Search tool helps customers find products based on photos, making it easier to discover new items.
- Chatbots for Customer Service: Sephora’s chatbot, powered by AI, offers instant support and guidance to customers. It can answer product-related questions, provide personalised beauty advice, and even help with order tracking and returns.
AI In Transportation
AI isn’t limited to the online world. Even the tangible offline world is leveraging the power of AI to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Here are some examples of AI in transportation:
- Self-Driving Cars: Companies like Tesla, Google, and Uber invest heavily in developing self-driving cars that use AI algorithms to analyse data from sensors, cameras, and other sources to navigate roads. This technology can potentially revolutionise transportation by reducing accidents and traffic jams.
- Predictive Maintenance: Using AI-powered sensors and predictive analytics, transportation companies can identify when a vehicle or equipment needs maintenance before a breakdown occurs. This not only saves time but also reduces maintenance costs.
- Maps and Navigation: AI-powered mapping and navigation tools like Google Maps use real-time data to provide the most efficient route to a destination. They also consider factors like traffic, accidents, and road closures to suggest alternate routes.
Example Of AI In Transportation: Waymo

Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. (Google’s parent company), is a leading self-driving technology company. The company focuses on developing fully self-driving vehicles that can operate without a human driver. Waymo’s AI system is trained using billions of miles of real-world driving data, making it one of the market’s most advanced and reliable solutions. The company has already launched its ride-hailing service in Phoenix, Arizona, and plans to expand to other cities soon.
Here are the key ways Waymo leverages AI in the transportation industry to develop its autonomous driving technology:
- Perception and computer vision: Waymo uses AI and machine learning algorithms to process data from its suite of sensors (lidar, cameras, radar) to perceive and understand the vehicle’s surroundings in real time. This allows the Waymo Driver to identify objects like pedestrians, vehicles, road signs, and obstacles.
- Behaviour prediction: Using deep learning (a subtype of AI that uses neural networks to understand and interpret data like a human brain), Waymo’s AI predicts the future behaviour and trajectories of objects around the vehicle, such as predicting the paths pedestrians and other cars may take.
- Route planning and decision making: Waymo’s AI takes all the perception data and behaviour predictions to plan the optimal route and make split-second driving decisions like when to brake, accelerate, or steer. The goal is to drive safely and efficiently to the destination.
AI In Education
AI is significantly disrupting and transforming traditional teaching methods, making education more personalised and effective. Here are some ways AI is being used in the education industry:
- Adaptive learning: With AI-powered adaptive learning systems, students can learn at their own pace and receive personalised feedback and recommendations based on their strengths and weaknesses.
- Intelligent tutoring: Virtual tutors powered by AI can provide one-on-one instruction to students, answering questions and providing explanations in a way that simulates human tutoring.
- Automated grading: AI-based grading systems can quickly evaluate student work and provide immediate feedback to help students improve their skills.
- Virtual assistants: Schools are increasingly using AI-powered virtual assistants to answer questions, provide information, and assist students with tasks.
- Personalised learning paths: AI can analyse students’ performance and preferences to create individualised learning plans tailored to their needs and interests.
Example Of AI In The Education Industry: Carnegie Learning
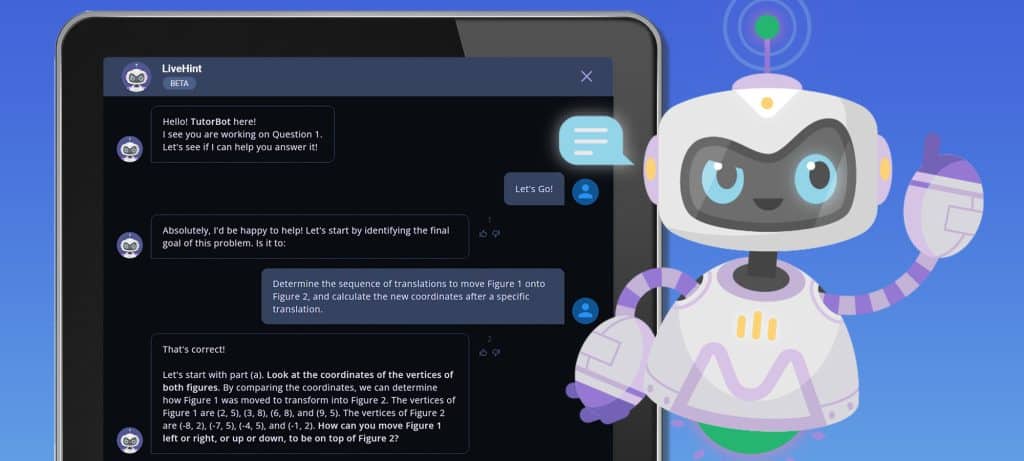
Carnegie Learning is an innovative edtech company that uses AI and cognitive science to create adaptive learning solutions for K-12 education, particularly in math and science.
Its product, MATHia®, provides personalised learning experiences by analysing student responses and offering targeted support. MATHia® analyses student responses and interactions with the platform to gain insights into their understanding of mathematical concepts. By assessing student performance data, the AI-driven system identifies areas where students struggle and provides targeted support and guidance.
Here’s how Carnegie Learning is disrupting the education industry:
- Personalised Learning: MATHia’s AI adapts to every student’s action, delivering real-time feedback and support. It is trained to recognise why students make specific mistakes so it can guide their thinking.
- Intelligent Tutoring: MATHia mirrors a human math coach through AI. It provides step-by-step guidance, rephrases questions, and focuses on the parts of problems proving difficult for the student, similar to a human tutor.
- Actionable Insights for Teachers: MATHia provides teachers with real-time data and actionable insights to effectively guide student learning. Teachers receive detailed views of student progress and predictive reporting.
- Behaviour prediction: Using deep learning (a subtype of AI that uses neural networks to understand and interpret data like a human brain), Waymo’s AI predicts the future behaviour and trajectories of objects around the vehicle, such as predicting the paths pedestrians and other cars may take.
AI In Marketing

The marketing industry has seen the most significant impact of AI in recent years. AI has revolutionised how businesses advertise, promote and sell their products or services. It isn’t limited to generative AI-powered product descriptions; it extends to creating personalised advertisements, analysing consumer data to predict and anticipate their needs, and providing real-time customer support. Here are some ways AI is disrupting marketing:
- Personalisation: AI enables businesses to create highly personalised marketing campaigns by analysing vast consumer data. For example, Amazon and Netflix use AI recommendation engines to suggest products and content to users based on their history and similar users’ behaviour.
- Predictive analytics: Machine learning models can predict which customers will most likely purchase, churn, or respond to an offer. For example, Mailchimp is developing a technology to predict which customers will most likely convert using several data points.
- Intelligent automation: AI automates many manual marketing tasks, such as ad buying, A/B testing, and even some content creation. For example, Facebook’s ad platform uses AI to show ads to the most relevant audience automatically.
- Voice search optimisation: With the rise of voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, businesses are optimising their websites and content for voice search. AI-powered natural language processing (NLP) tools help optimise content for voice queries, which are longer and more conversational than text-based searches.
- Chatbots: Chatbots use NLP to understand and respond to customer queries like humans. They can handle multiple conversations simultaneously and provide quick responses, improving customer service and engagement.
Example Of AI In Marketing: Starbucks
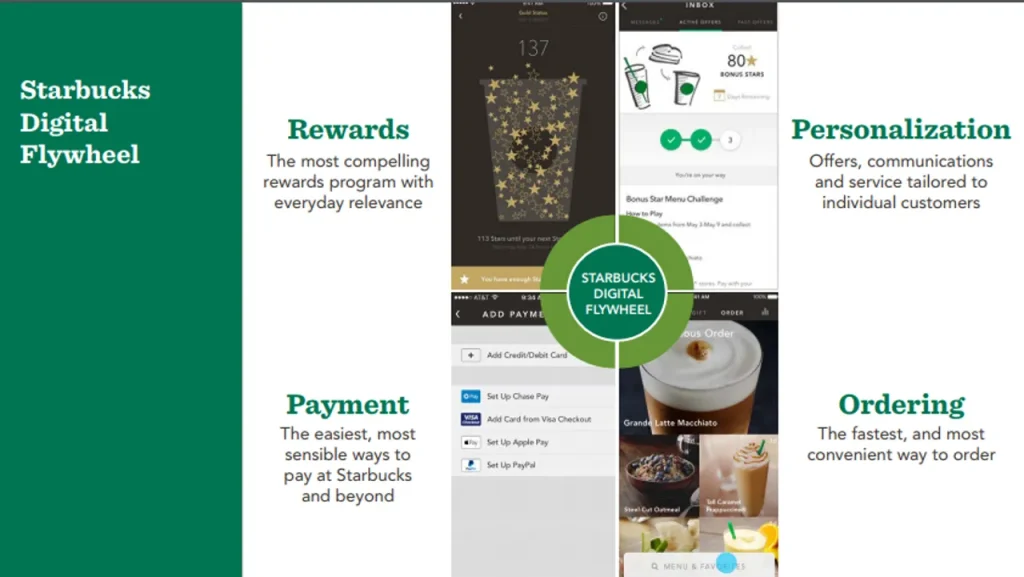
Starbucks is a great example of a brand leveraging AI to disrupt marketing. Their “Digital Flywheel” program uses predictive analytics and machine learning to drive personalised offers and recommendations across their app, website and email.
Starbucks’ ability to collect and analyse vast amounts of customer data is at the core of the Digital Flywheel. The company gathers data from multiple touchpoints, including its mobile app, website, email interactions, point-of-sale systems, and even external factors like weather. This rich data is then fed into sophisticated machine-learning models that predict customer preferences and behaviours.
Some key ways Starbucks uses AI in the Digital Flywheel:
- Personalised product recommendations – The AI analyses customers’ past purchases, browsing history, and contextual data to recommend products they will most likely enjoy. These recommendations are surfaced across the app, website, and email to drive incremental purchases.
- Customised offers and rewards – Predictive models determine which offers, discounts, or rewards will appeal to each customer based on their habits and preferences. This increases the relevance and redemption rates of promotions.
- Tailored content and communications – Starbucks personalises the content, creative, and timing of its digital communications for each customer. For example, the app homepage and featured products may change based on the user’s favourite items, time of day, or local weather.
- Optimised store inventory – AI helps Starbucks predict demand for specific products at each store location, down to the hour. This ensures the right items are always in stock and reduces waste.
- New product development – By analysing customer data and predicting trends, Starbucks can develop new products more likely to resonate with its customer base.
AI In Entertainment Industry

Even the entertainment industry is embracing AI to create more engaging and personalised consumer experiences. From music and film production to video games and live performances, AI is revolutionising the way entertainment is created and consumed. Here are some key ways AI is being used in the entertainment industry:
- Content creation – AI algorithms can analyse vast amounts of data on past successes, consumer preferences, and trends to generate ideas for new content such as songs, movie scripts or video game levels. For example, Suno.ai is a proprietary model that lets users input parameters for a song and generates a brand new track – including lyrics, background music, and vocals.
- Personalised recommendations – OTT platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime and Hulu use AI to curate personalised content recommendations based on user viewing habits, ratings, and other data points. This helps users discover new shows or movies they are likely to enjoy.
- Visual effects—Hollywood is increasingly using AI to create realistic visual effects that were previously impossible. For example, Thanos in Avengers: Endgame was created using Artificial Intelligence techniques instead of traditional animation methods.
- Personalised content – Tools like ChatGPT, Eleven Labs and Synthesia are using AI to create personalised content experiences for users. For example, you can create a personalised video with your face and voice without even recording yourself. You can generate the script using ChatGPT, convert it into your voice using Eleven Labs, and use Synthesia to create a video with your face – all powered by AI.
AI In the Entertainment Industry Example: Netflix
Netflix’s biggest competitor isn’t Amazon Prime, Hulu, or any other OTT platform – it’s actually your sleep. As an online streaming platform, Netflix has faced challenges in keeping subscribers engaged for longer periods. This is where AI comes into play.
- Personalised Recommendations: Netflix’s AI-powered recommendation system is central to its user experience. It analyses vast amounts of data, including viewing history, ratings, searches, and time spent, to curate personalised content suggestions for each user. The algorithms identify patterns to understand user preferences and recommend titles that align with their interests.
- Thumbnail Personalisation: Netflix uses ML to select the most appealing thumbnail images for each title based on a user’s viewing habits. The AI annotates and ranks frames from videos to determine the optimal thumbnails most likely to entice a user to watch, enhancing click-through rates and user engagement.
- Content Creation and Acquisition: Netflix employs predictive analytics and AI to inform content creation and acquisition strategies. By analysing user data, viewing trends, and social media buzz, Netflix can identify promising content opportunities and make data-driven decisions on which original series or movies to produce. For example, the decision to create “House of Cards” was based on data showing many users enjoyed political dramas, the original British version, and movies starring Kevin Spacey.
A startup consultant, digital marketer, traveller, and philomath. Aashish has worked with over 20 startups and successfully helped them ideate, raise money, and succeed. When not working, he can be found hiking, camping, and stargazing.









